2 Instructions
2-264
CP1E CPU Unit Instructions Reference Manual(W483)
PID control
Proportional Action (P)
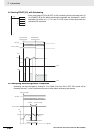
Proportional action is an operation in which a proportional band is established with respect to the set
value (SV), and within that band the manipulated variable (MV) is made proportional to the deviation.
An example for reverse operation is shown in the following illustration.
If the proportional action is used and the present value (PV) becomes smaller than the proportional
band, the manipulated variable (MV) is 100% (i.e., the maximum value). Within the proportional band,
the MV is made proportional to the deviation (the difference between from SV and PV) and gradually
decreased until the SV and PV match (i.e., until the deviation is 0), at which time the MV will be at the
minimum value of 0% (or 50%, depending on the setting of the manipulated variable output designation
parameter). The MV will also be 0% when the PV is larger than the SV.
The proportional band is expressed as a percentage of the total input range. The smaller the propor-
tional band, the larger the proportional constant and the stronger the corrective action will be. With pro-
portional action an offset (residual deviation) generally occurs, but the offset can be reduced by making
the proportional band smaller. If it is made too small, however, hunting will occur.
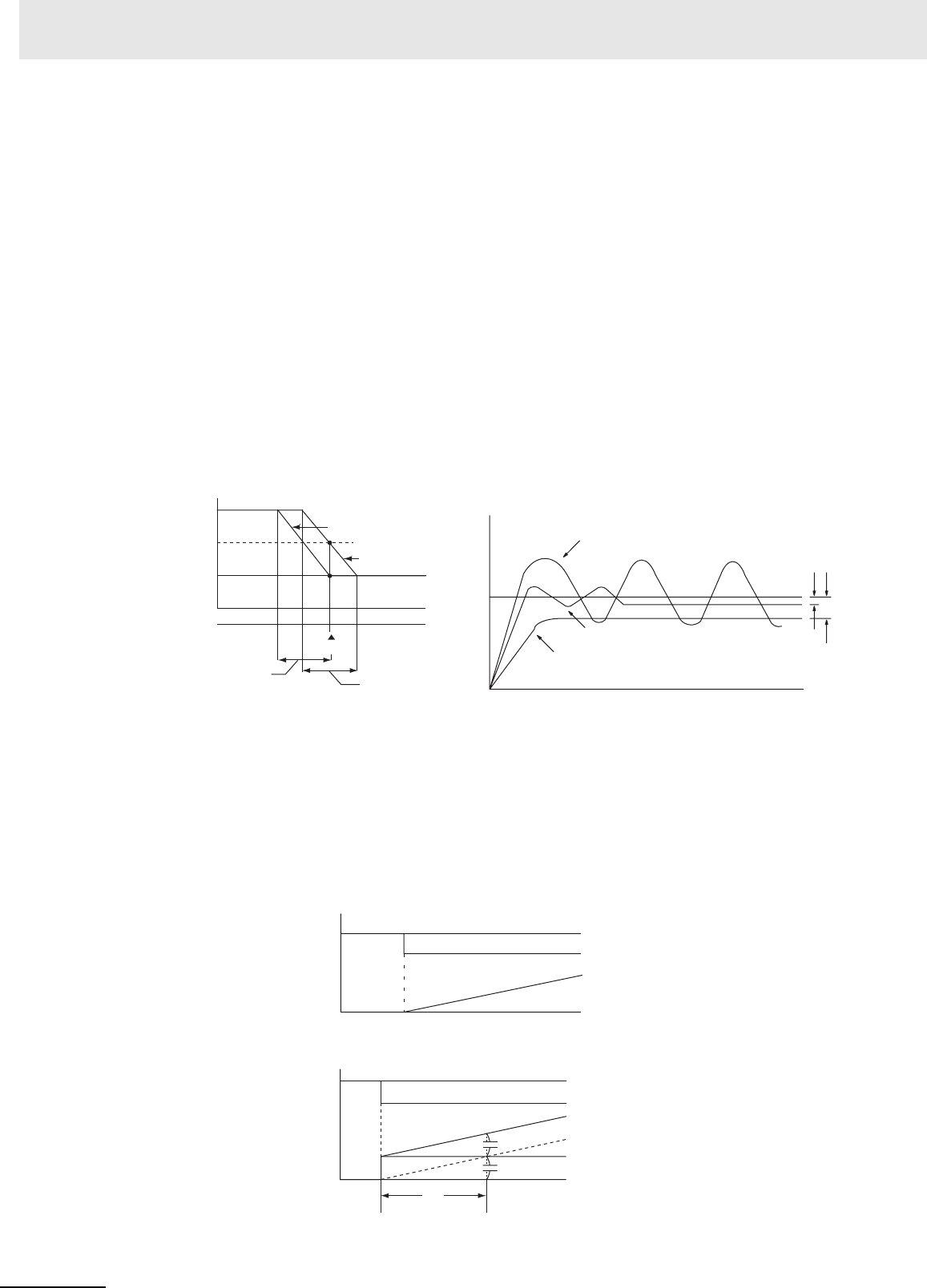
Integral Action (I)
Combining integral action with proportional action reduces the offset according to the time that has
passed, so that the PV will match the SV. The strength of the integral action is indicated by the integral
time, which is the time required for the manipulated variable of the integral action to reach the same
level as the manipulated variable of the proportional action with respect to the step deviation, as shown
in the following illustration. The shorter the integral time, the stronger the correction by the integral
action will be. If the integral time is too short, the correction will be too strong and will cause hunting to
occur.
SV
Adjusting the Proportional Band
Proportional Action (Reverse Action)
Proportional band too narrow (hunting occurring)
Offset
Proportional band just right
Proportional band too wide (large offset)
100%
50%
0%
Manipulated variable
Set point
Proportional band when
MV output designation is
0 (output 0%)
Proportional band when
MV output designation is
1 (output 50%)
Proportional band when
MV output designation is
1 (output 50%)
Proportional band when
MV output designation is
0 (output 0%)
0
0
PI action
P action
Step response
I action
Integral Action
Step response
Ti:
Integral time
Manipulated
variable
Deviation
Manipulated
variable
Deviation
Pi Action and Integral Time
0
0
Ti