2 – General Description
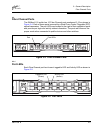
Fibre Channel Ports
2-6 59021-08 B
D
2.2.1.1
Port Logged-In LED
The Logged-in LED indicates the logged-in or initialization status of the connected
devices. After successful completion of the POST, the switch extinguishes all
Logged-In LEDs. Following a successful loop initialization or port login, the switch
illuminates the corresponding logged-in LED. This shows that the port is properly
connected and able to communicate with its attached devices. The Logged-In
LED remains illuminated as long as the port is initialized or logged in. If the port
connection is broken or an error occurs that disables the port, the Logged-In LED
will flash. Refer to ”Logged-In LED Indications” on page 5-6 for more information
about the Logged-In LED.
2.2.1.2
Port Activity LED
The Activity LED indicates that data is passing through the port. Each frame that
the port transmits or receives causes this LED to illuminate for 50 milliseconds.
This makes it possible to observe the transmission of a single frame. When
extending credits, the Activity LED for a donor port will reflect the traffic of the
recipient port. Refer to ”Distance” on page 3-4 for more information about
extended credits and donor ports.
2.2.2
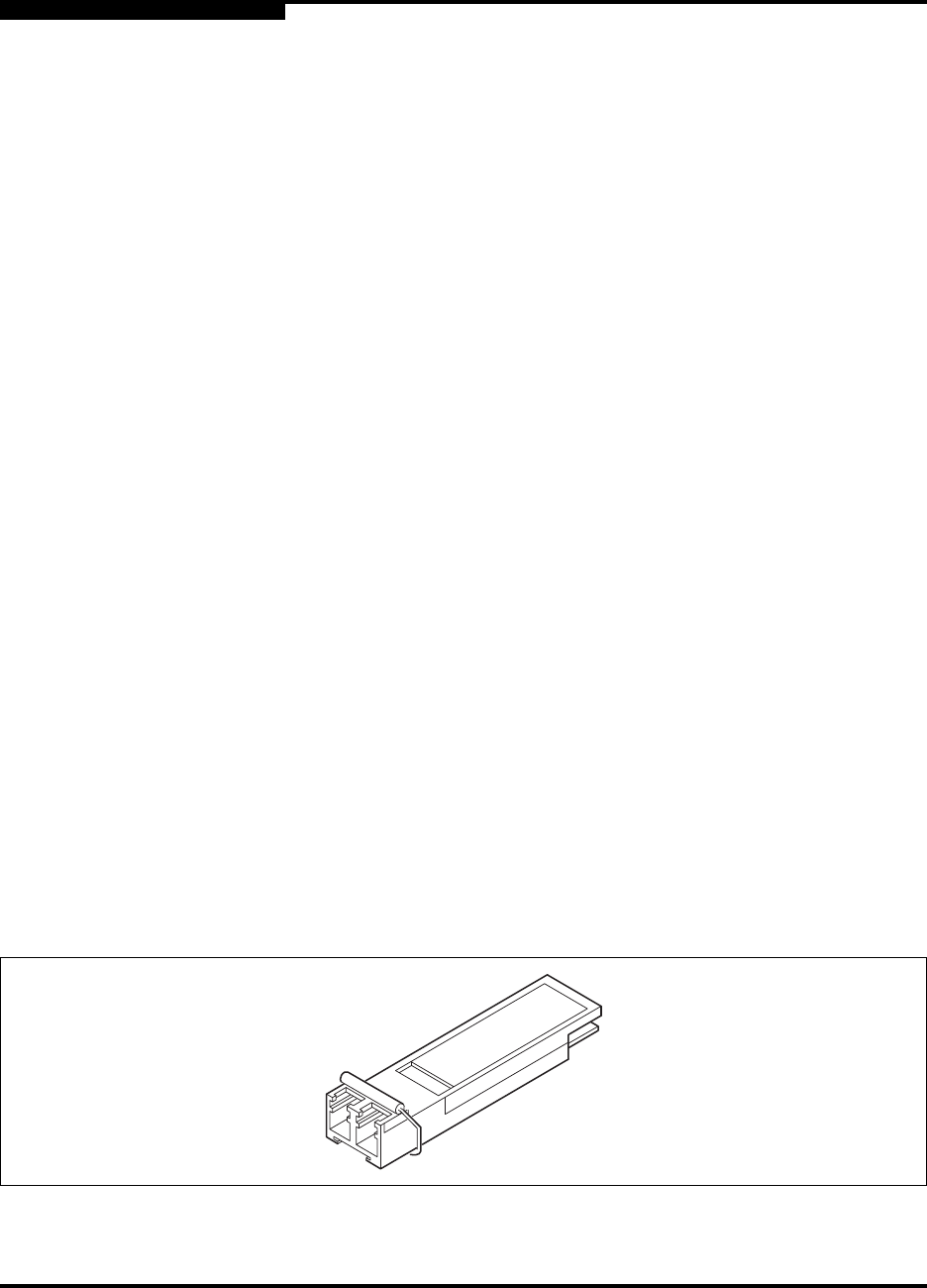
Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceivers
An SFP transceiver, like the one shown in Figure 2-6, converts electrical signals to
and from optical laser signals to transmit and receive. SFP transceivers plug into
the ports; duplex fiber optic cables plug into the transceivers which then connect
to the devices. A port is capable of transmitting at 1 Gbps or 2 Gbps; however, the
transceiver must be capable of 2 Gbps for the port to deliver at that rate.
The SFP transceivers are hot pluggable. This means that you can remove or
install an SFP transceiver while the switch is operating without harming the switch
or the transceiver. However, communication with the connected device will be
interrupted. Refer to ”SFP Transceivers” on page 6-2 for information about
installing and removing SFP optical transceivers.
Figure 2-6. SFP Transceiver