Removal and replacement procedures 26
Hard drive blanks
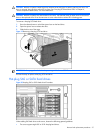
To remove a hard drive blank:
1. Push the sliding release button to unlock the blank .
2. Pull the drive blank out of the drive cage .
Figure 18 Removing a drive blank
NOTE: Keep the blank for future use.
Reverse the steps to replace a drive blank.
Hot-plug SCSI hard drives
Drive replacement precautions
Be aware of the following guidelines cautioning unsafe hot-plug replacement.
• Do not remove a degraded drive if any other member of the array is offline (the online LED is off). No other
drive in the array is hot-pluggable without data loss. The exception to this is the use of RAID 1+0 as a fault-
tolerant configuration. In this case, drives are mirrored in pairs. More than one drive can fail and be replaced
as long as the drive or drives they are mirroring are online.
• Do not remove a degraded drive if any member of an array is missing (removed previously and not yet
replaced).
• Do not remove a degraded drive if any member of an array is being rebuilt, unless the drive being rebuilt has
been configured as an online spare. The online LED for the drive flashes green or amber, indicating that a
replaced drive is being rebuilt from the data stored on the other drives.
NOTE: An online spare drive does not activate and start rebuilding after a predictive failure alert because the
degraded drive is still online. The online spare activates only after a drive in the array has failed.
• Do not replace multiple degraded drives at the same time because the fault tolerance can be compromised.
When a drive is replaced, the controller uses data from the other drives in the array to reconstruct data on the
replacement drive. If more than one drive is removed, a complete data set is not available to reconstruct data
on the replacement drive or drives, and permanent data loss can occur.
CAUTION: Do not turn off any external unit when the server containing. A Smart Array controller is powered
up. Also, do not power up the server before powering up the drive enclosure. If these ordering rules are not
followed, the Smart Array controller might mark the drives in this enclosure as failed, resulting in permanent
data loss.