TANDBERG Border Controller User Manual
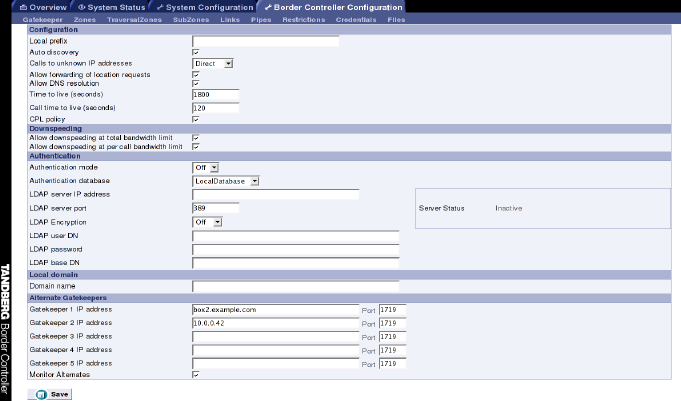
Figure 2: Alternate Border Controller configuration
3.5 Call Control
When an endpoint wants to call another endpoint it presents the address it wants to call to
the Border Controller using a protocol knows as RAS. The Border Controller tries to resolve
this address and supplies the calling endpoint with information about the called endpoint. The
destination address can take several forms: IP address, H.323 ID, E.164 alias or a full H.323
URI.
When an H.323 ID or E.164 alias is used, the Border Controller looks for a match between the
dialed address and the aliases registered by its endpoints. If no match is found, it may query
other Gatekeepers and Border Controllers.
When dialing by H.323 URI, the destination address resembles an email address. The Border
Controller first follows the procedure for matching H.323 IDs. If that fails it looks for a Gatekeeper
or Border Controller responsible for the domain (the part of the URI following the @ symbol) and
queries that device.
Dialing by IP address is necessary when the destination endpoint is not registered with a
Gatekeeper or Border Controller. If it is registered, then one of the other addressing schemes
should be used instead as they are more flexible. From your registered endpoint, dial the
IP address of the endpoint you wish to call. This requires that the Border Controller has
xConfiguration Gatekeeper CallToUnknownIPAddresses correctly configured.
It is not possible to dial endpoints behind a Border Controller by IP address. Calls should be
made using an E.164 or H.323 alias.
Figure 3 illustrates the process the Border Controller performs when receiving call requests:
11


















