DED[31:0]
DSDDQS[3:0]
COL
BANK
DQM7
Sample
D0
D1 D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
DQM1 DQM2 DQM3 DQM4 DQM5 DQM6 DQM8
WriteLatency
DEA[10]
DDR2CLKOUT
DDR2CLKOUT
DCE0
DSDCKE
DSDRAS
DSDWE
DSDDQM[3:0]
DSDCAS
DBA[2:0]
DEA[13:0]
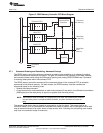
Peripheral Architecture
www.ti.com
2.4.6 Write (WRT) Command
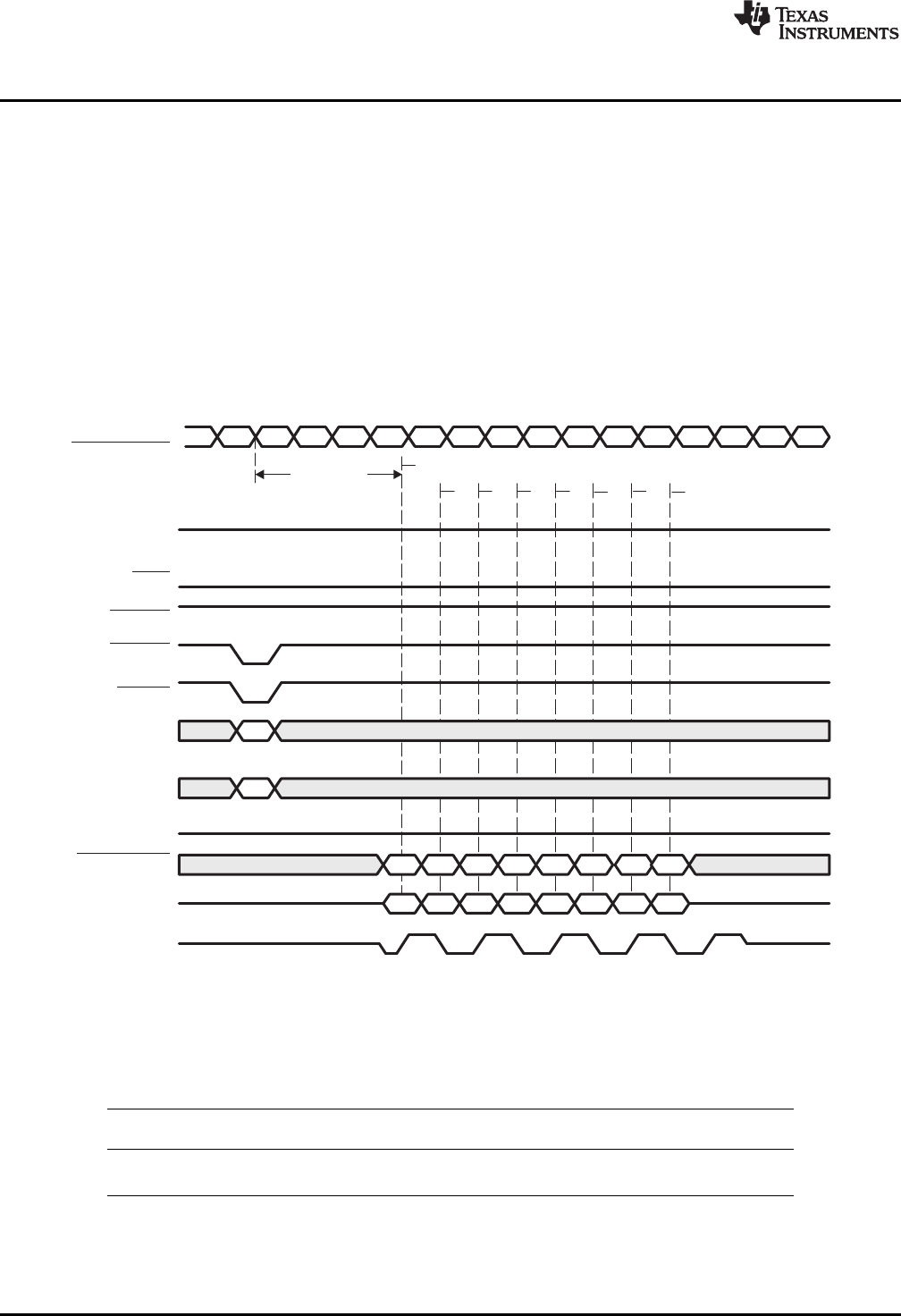
Prior to a WRT command, the desired bank and row are activated by the ACTV command. Following the
WRT command, a write latency is incurred. Write latency is equal to CAS latency minus 1. All writes have
a burst length of 8. The use of the DSDDQM outputs allows byte and halfword writes to be executed.
Figure 9 shows the timing for a write on the DDR2 memory controller.
If the transfer request is for less than 8 words, depending on the scheduling result and the pending
commands, the DDR2 memory controller can:
• Mask out the additional data using DSDDQM outputs
• Terminate the write burst and start a new write burst
The DDR2 memory controller does not perform the DEAC command until page information becomes
invalid.
Figure 9. DDR2 WRT Command
2.5 Memory Width, Byte Alignment, and Endianness
The DDR2 memory controller supports memory widths of 16 bits and 32 bits. Table 4 summarizes the
addressable memory ranges on the DDR2 memory controller.
Table 4. Addressable Memory Ranges
Memory Width Maximum Addressable Bytes Address Type Generated by DDR2
Memory Controller
×16 256M bytes Halfword address
×32 512M bytes Word address
20
C6455/C6454 DDR2 Memory Controller SPRU970G–December 2005–Revised June 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2005–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated