56
Setting Up DDNS
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) is a service that provides a static address to simplify remote connection to the recorder. This
service is most useful for installations where the WAN (public) IP address is dynamic (changes from time to time). Most public IP
addresses are dynamic unless a static address has been specifically ordered from the internet service provider.
Enable DDNS
To enable this functionality of the recorder, follow the steps below:
1. Click Setup on the Display screen and log in as Administrator if prompted.
2. Click Administrative.
3. Click Program Management (ETC) and enter the Administrator password when prompted.
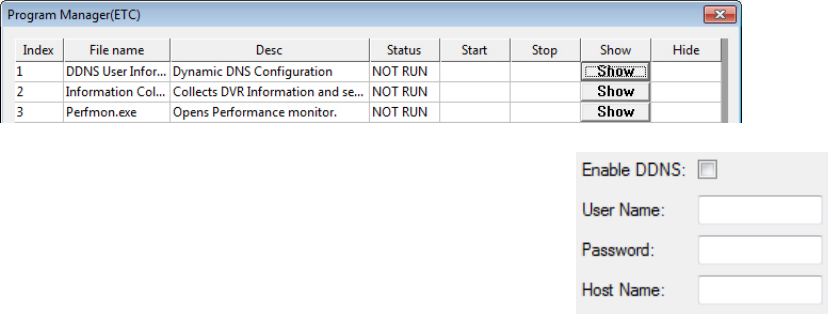
4. Click Show (to the right of Dynamic DNS Configuration).
5. Select Enable DDNS.
6. Enter the User Name, Password, and Hostname specified on the DDNS document
shipped with your recorder.
7. Click OK, then close the Program Manager window.
Note Ensure the recorder has an IP address by setting it statically. The Network settings may
need to be changed. If you are not sure of the correct values, contact the individual or
department responsible for network administration at the site.
Set the IP Address
The IP address of the recorder is set in Windows; to set the IP address follow the steps below:
1. On the Display screen, click Exit and choose Restart in Windows Mode.
2. Right-click My Network Places and click Properties.
3. On the General tab, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click Properties.
4. Select Use the following IP address.
5. Enter values for the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway (these may be specified by the department responsible
for network administration).
a. IP Address: The first three sets of numbers should match the router’s local IP address and the last set should
be a unique number between 1-254.
b. Subnet Mask: This should match the router’s setting (commonly 255.255.255.0 for 192.X addresses and
255.0.0.0 for 10.X addresses).
c. Default Gateway: This is the router’s internal IP address. Once DDNS is configured, the router the recorder
connects to will need to have port forwarding configured.
For further instruction on this process, visit http://www.portforeward.com/english/routers/port_forwarding/outerindex.htm
Once DDNS and port forwarding have been configured, the recorder will be accessible from any remote site by entering the HOSTNAME
into the address bar of Internet Explorer or the IP Address field in remote software.