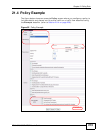
Chapter 22 Queuing Method
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
216
2
(Weight -1)
x 10 KB
If the weight setting is 5, the actual quantum guaranteed to the associated queue
would be as follows:
2
4
x 10KB = 160 KB
22.1.3 Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR)
Round Robin Scheduling services queues on a rotating basis and is activated only
when a port has more traffic than it can handle. A queue is given an amount of
bandwidth irrespective of the incoming traffic on that port. This queue then moves
to the back of the list. The next queue is given an equal amount of bandwidth, and
then moves to the end of the list; and so on, depending on the number of queues
being used. This works in a looping fashion until a queue is empty.
Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) uses the same algorithm as round robin
scheduling, but services queues based on their priority and queue weight (the
number you configure in the queue Weight field) rather than a fixed amount of
bandwidth. WRR is activated only when a port has more traffic than it can handle.
Queues with larger weights get more service than queues with smaller weights.
This queuing mechanism is highly efficient in that it divides any available
bandwidth across the different traffic queues and returns to queues that have not
yet emptied.