Chapter 38 IGMP
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
346
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is used by multicast hosts to indicate
their multicast group membership to multicast routers. Multicast routers can also
use IGMP to periodically check if multicast hosts still want to receive transmission
from a multicast server. In other words, multicast routers check if any hosts on
their network are still members of a specific multicast group.
The Switch supports IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1), version 2 (IGMP-v2) and IGMP
version 3 (IGMP-v3). Refer to RFC 1112, RFC 2236 and RFC 3376 for information
on IGMP versions 1, 2 and 3 respectively. At start up, the Switch queries all
directly connected networks to gather group membership. After that, the Switch
periodically updates this information.
38.1.1 How IGMP Works
This section describes how IGMP works and the changes it has gone through from
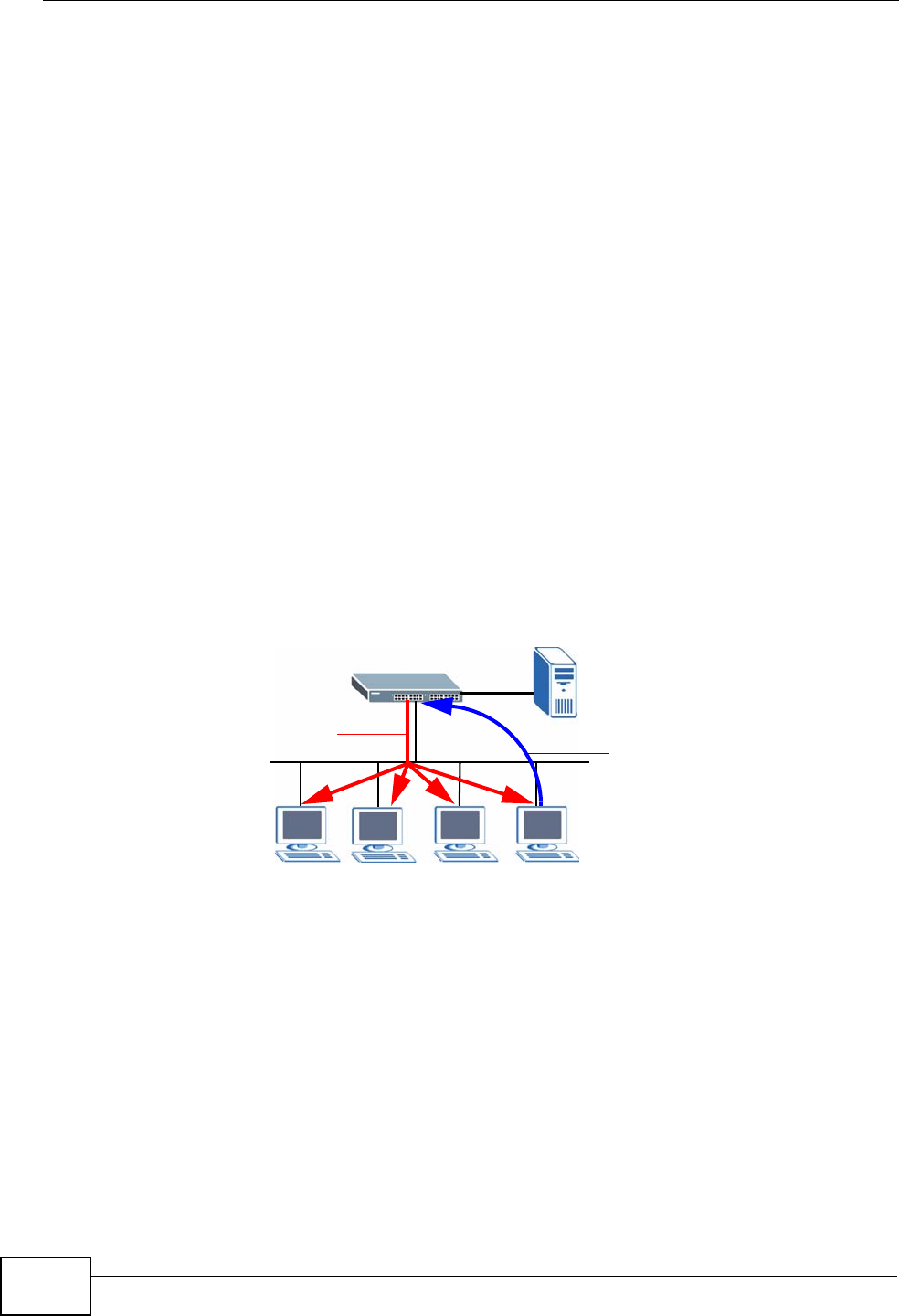
version 1 to version 3. IGMP version 1 defines how a multicast router checks to
see if any multicast hosts are part of a multicast group. It checks for group
membership by sending out an IGMP Query packet. Hosts that are members of a
multicast group reply with an IGMP Report packet. This is also referred to as a join
group request. The multicast router then keeps a list of all networks that have
members of this multicast group and forwards multicast traffic to that network.
Figure 169 IGMP Version 1 Example
The main difference in IGMP version 2 is that it provides a mechanism for a
multicast group member to notify a multicast router that it is leaving a multicast
group. The multicast router then sends a group-specific IGMP query to check if
there are any members remaining in that group. If the multicast router does not
receive an IGMP report from any members, it stops sending multicast traffic to
that group. This change helps shorten the leave convergence time, in other words,
the amount of time that a multicast router believes that there are group members
2 Report
1 Query


















