Chapter 40 Differentiated Services
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
354
kinds of traffic can be marked for different priorities of forwarding. Resources can
then be allocated according to the DSCP values and the configured policies.
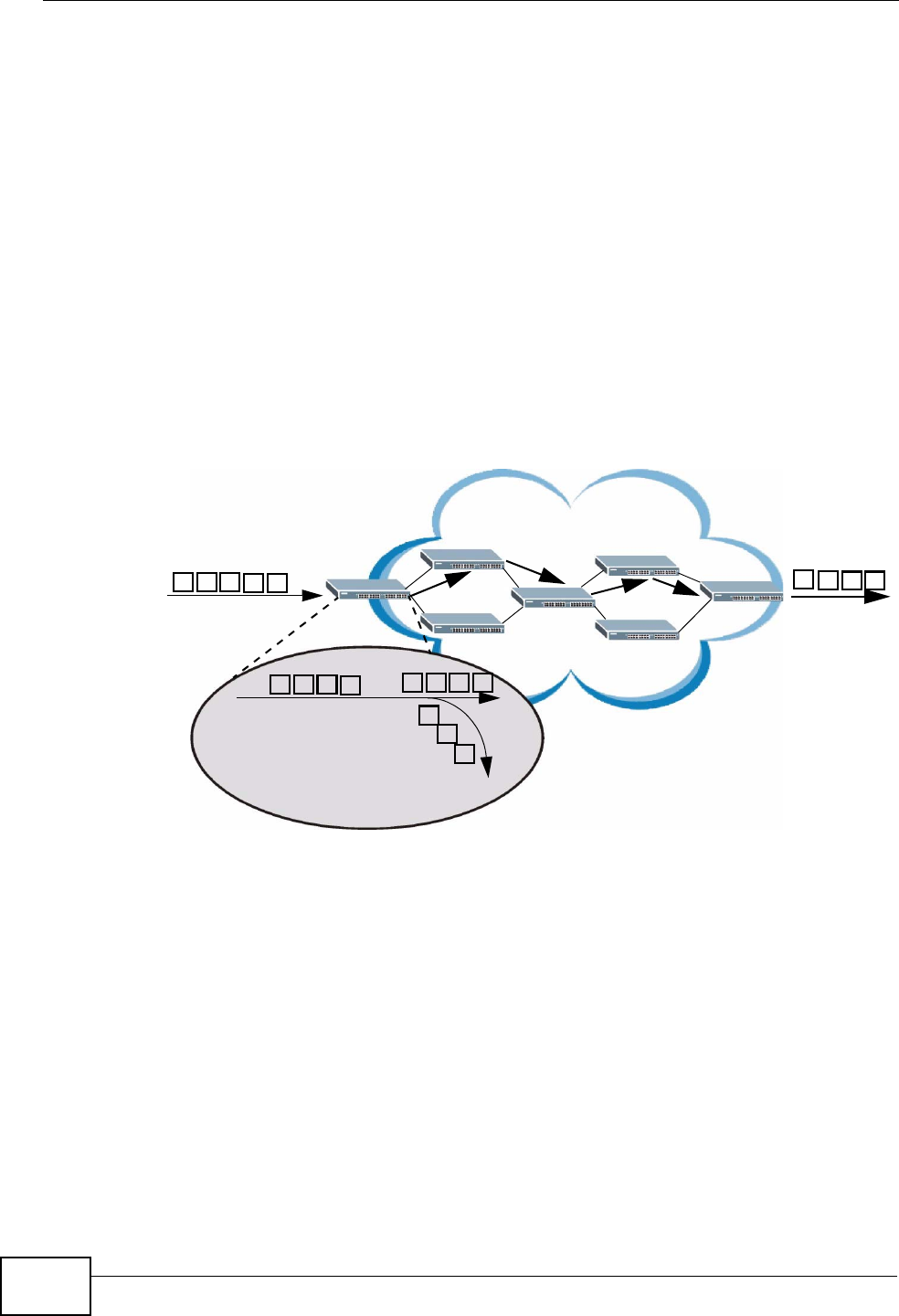
40.1.2 DiffServ Network Example
The following figure depicts a DiffServ network consisting of a group of directly
connected DiffServ-compliant network devices. The boundary node (A in Figure
179) in a DiffServ network classifies (marks with a DSCP value) the incoming
packets into different traffic flows (Platinum, Gold, Silver, Bronze) based on the
configured marking rules. A network administrator can then apply various traffic
policies to the traffic flows. For example, one traffic policy would be to give higher
drop precedence to one traffic flow over others. In our example packets in the
Bronze traffic flow are more likely to be dropped when congestion occurs than the
packets in the Platinum traffic flow as they move across the DiffServ network.
Figure 179 DiffServ Network
40.2 Two Rate Three Color Marker Traffic
Policing
Traffic policing is the limiting of the input or output transmission rate of a class of
traffic on the basis of user-defined criteria. Traffic policing methods measure traffic
flows against user-defined criteria and identify it as either conforming, exceeding
or violating the criteria.
Two Rate Three Color Marker (TRTCM, defined in RFC 2698) is a type of traffic
policing that identifies packets by comparing them to two user-defined rates: the
Committed Information Rate (CIR) and the Peak Information Rate (PIR). The CIR
G
S
B
P
S
B
B
G
P
P
S
P - Platinum
G - Gold
S - Silver
B - Bronze
G
P
P
S
A


















