ADVANCED MICRO SYSTEMS, INC. SERIAL INTERFACE
20
4. Party Select (pin 8). Each axis tests this input after reset (power up or in response to a ^C command) to
determine either single or party line mode. Single mode (ONLY one axis connected) is used for debug,
programming for stand-alone use or assignment of party line “name”. The SIN-8 has a switch to manually
select party line (P) or Single (S) mode. The SIN-10 is selectable via host commands or a built in mode
switch.
Serial Communications Overview
There are three methods (protocols) used to send and receive command and data from an AMS controller
(axis):
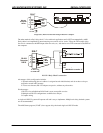
1. Simple “Dumb” Communications
This is accomplished by connecting one single axis to the computer. Commands can be typed in and the
controller will execute them. The designer can also enter program sequences into the NV memory and
execute them. Virtually every capability can be explored. It is a “human friendly” interface and NEVER a
computer controlled operation.
Serial adapters used: SIN-7 / SIN-9, SIN-8, or SIN-10.
At start-up:
1. If using a SIN-8 or SIN-10 serial adapter, make sure it is in “single-line” mode.
2. Hit the SPACE BAR key to sign on after reset.
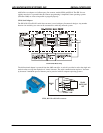
2. Party Line Mode
Party line mode is intended for computer-controlled designs. A computer (usually a PC) can address one or
more axis using a “mini drop” network implemented with CAT-5 network cable with RS-422/485.
Between 1 and 32 axis are configured as “slaves.” Unlike the “Dumb” mode, a proper character by character
echoed protocol is necessary for proper operation. The SIN-10 adapter will simplify this protocol.
Serial adapter used: SIN-8 or SIN-10.
At start-up:
1. Make sure the serial adapter is in “party line” mode.
2. The host computer interrogates and records axis name(s).
3. Daisy Chain Mode (not recommended for more than 1 axis)
This older protocol is similar to the party line mode but RS-232 protocol is used. Because it involves special
wiring of RXD to TXD signals, it should only be used with a single axis design. When multiple axis are
implemented they are less reliable, communication speeds are slower and troubleshooting is difficult.
The only advantage is that the name can be dynamically assigned by the host computer on power up
sequence and the computer protocol can be implemented with the lowest cost RS-232 adapters.
Serial adapters used: SIN-7 or SIN-9.
At start-up:
1. The host computer emits axis #1 name, receives ending axis name +1.
Serial Communications Software
Today’s computers are mostly a derivative of the IBM PC. Almost all of these computers include at least
one serial RS-232 connection. For those without “COM” ports, low cost serial cards are available.
For many years PC’s have used DOS as the basic operating software. In recent years however, Windows
has replaced DOS in many applications. So, the system designer must make choices about the application
requirements.