ADVANCED MICRO SYSTEMS, INC. SMC-27X2 SOFTWARE
44
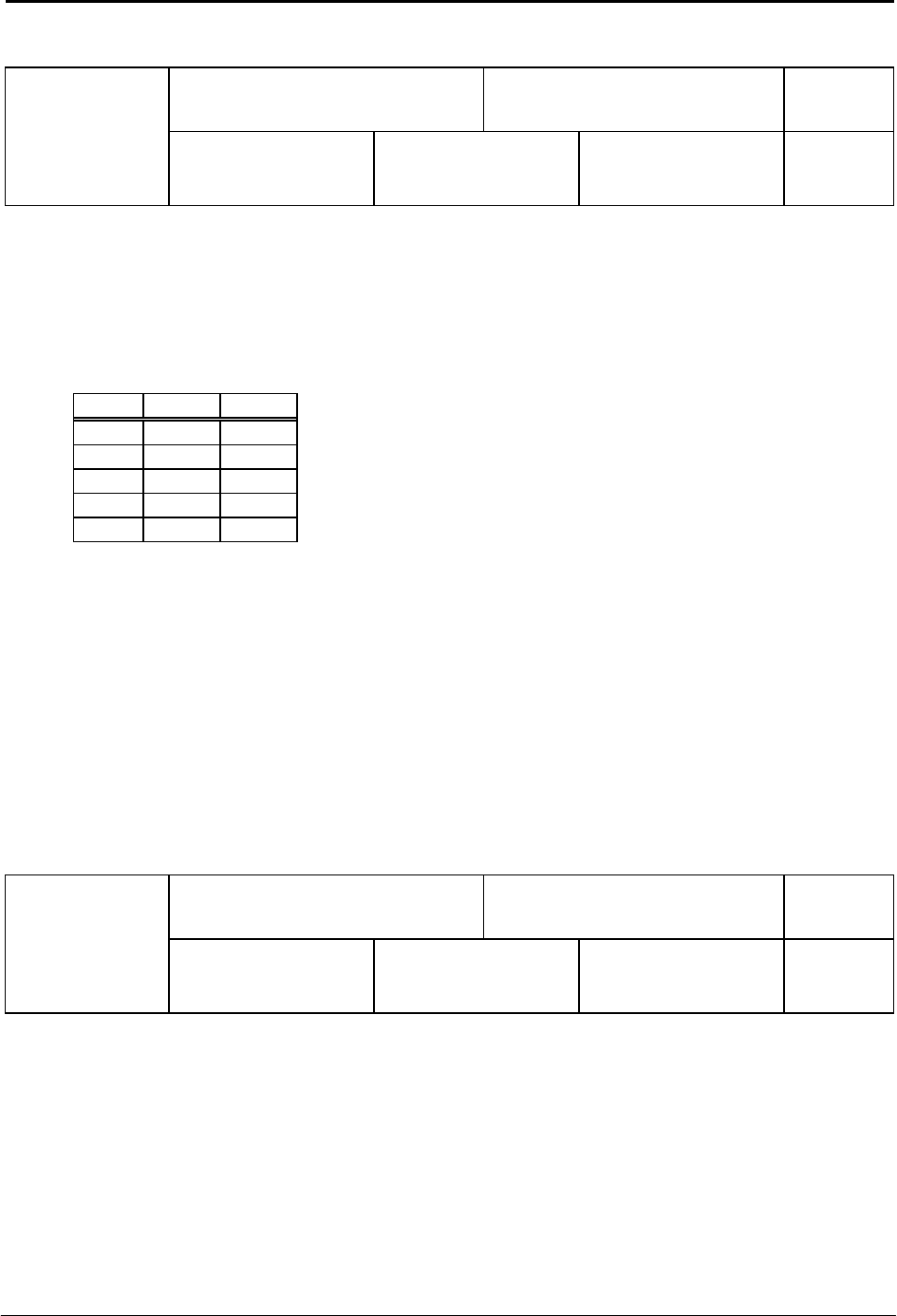
Function Type NV Bytes
Loop on Port Program 3
Command
L
Mnemonic
(Name) L (a, c)
Data 1
0-2048
Data 2
Condition (0-9)
Result
None
L (Loop on Port)
Loop on Port will test the specified input port for the required condition (c). If the port is NOT at the
required level then the program will jump to the specified address. If the address is to a previous instruction
then the program will loop until it becomes the specified level. The program will then continue to the next
step. The PLC mode inverts the input high/low definitions.
Input ports are available as follows:
Port Low High
1 0 1
2 2 3
3 4 5
4 6 7
5 8 9
The SMC-27X2 can view all ports as inputs and outputs, restricted by contention with external hardware.
Any “output” port can be modified, then subsequently used in conjunction with the L, G 2048, or A129
(read) command. The SMC-27X2 has an additional feature of implementing a “wait till” function. The
standard loop tests the condition every 2-3ms. If the unique address is 2048, the controller executes a tight
loop at this instruction, monitoring the specified condition. When the condition is met, program execution
continues.
This feature is helpful in situations where the condition may be of short duration. This command is usable
only in NV memory program execution. Following is an example of this command:
P 0 Enter program mode.
L0 4 Stay at location 0 until port 3 is low then go to next command in program.
+ 1000 Move 1000 steps in the plus direction.
P Exit program mode.
Function Type NV Bytes
Hardware Options Default, Immediate, Program 2
Command
l
Mnemonic
(Name) l (a, d)
Data 1
Option Flags
Data 2
Result
None
l (lower case L; Option Flags)
IMPORTANT – DO NOT CHANGE JUMPERS WITH POWER APPLIED
This command configures several options, primarily relating to input/output operating modes and defining
external hardware. Several options invert the sense of input signals. If appropriate jumpers or input signal
inversion is not matched to the selected option(s) then the system may lock up or motion can be inhibited.
Flags and Numbers
Several commands use “on-off” flags to enable or disable some feature. The data supplied is in decimal
ranging between 0 and 255. The corresponding binary bits are called flags. There are 8 flags, each equaling
binary values of 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128.