VIP-4R/4T Installation and Configuration 5
Versatile Interface Processor Functions
VIP Software Prerequisites
The VIP requires that the host Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series router is running Cisco
Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) Release 11.1(1) or later, or a Cisco-approved beta
version of Cisco IOS Release 11.1.
Note The latest Cisco IOS release is available via anonymous File Transfer Protocol (FTP) from
ftp/beta111_dir@ftp.cisco.com. Detailed information about the latest Cisco IOS release can be
found in the ASCII file vip1-readme, which is also available via FTP from ftp.cisco.com in the
directory /ftp/beta111_dir. This ASCII file includes information and instructions on how to get
the current Cisco IOS software images and VIP microcode. To access information located in Cisco
Information Online (CIO), refer to the section “Cisco Information Online” at the end of this
publication.
VIP Hardware Prerequisites
The VIP operates with the CxBus in the Cisco 7000 series and CyBus in the Cisco 7500 series, and
operates with the optional RSP7000 and RSP7000CI RSP-based processor modules in the Cisco
7000 series routers: Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010. The VIP will also operate with the Route Processor
(RP) and Switch Processor (SP) in the Cisco 7000 series routers. The VIP operates with all
RSP-based processor modules currently shipping in the Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series
routers: Cisco 7505, Cisco 7507, and Cisco 7513.
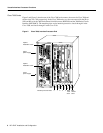
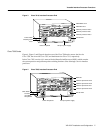
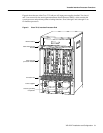
What is the Cisco 7000 Family?
For the Cisco 7000 family of routers, which includes the Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series
routers, network interfaces reside on modular interface processors, including the VIP, which provide
a direct connection between external networks and the high-speed CxBus in the Cisco 7000 series
and the high-speed CyBus in the Cisco 7500 series.
In all systems, the remaining slots support any combination of network interface types: Ethernet
attachment unit interface (AUI), Ethernet 10BASE-T, Fast Ethernet 100BASE-TX, Asynchronous
Transfer Mode (ATM), Token Ring, multichannel applications, Fiber Distributed Data Interface
(FDDI), channel attachment, serial, or High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI), and all VIP–based
interfaces.