4. Troubleshooting (PROFIBUS DP)
♦ Causes of Error
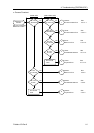
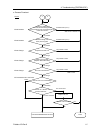
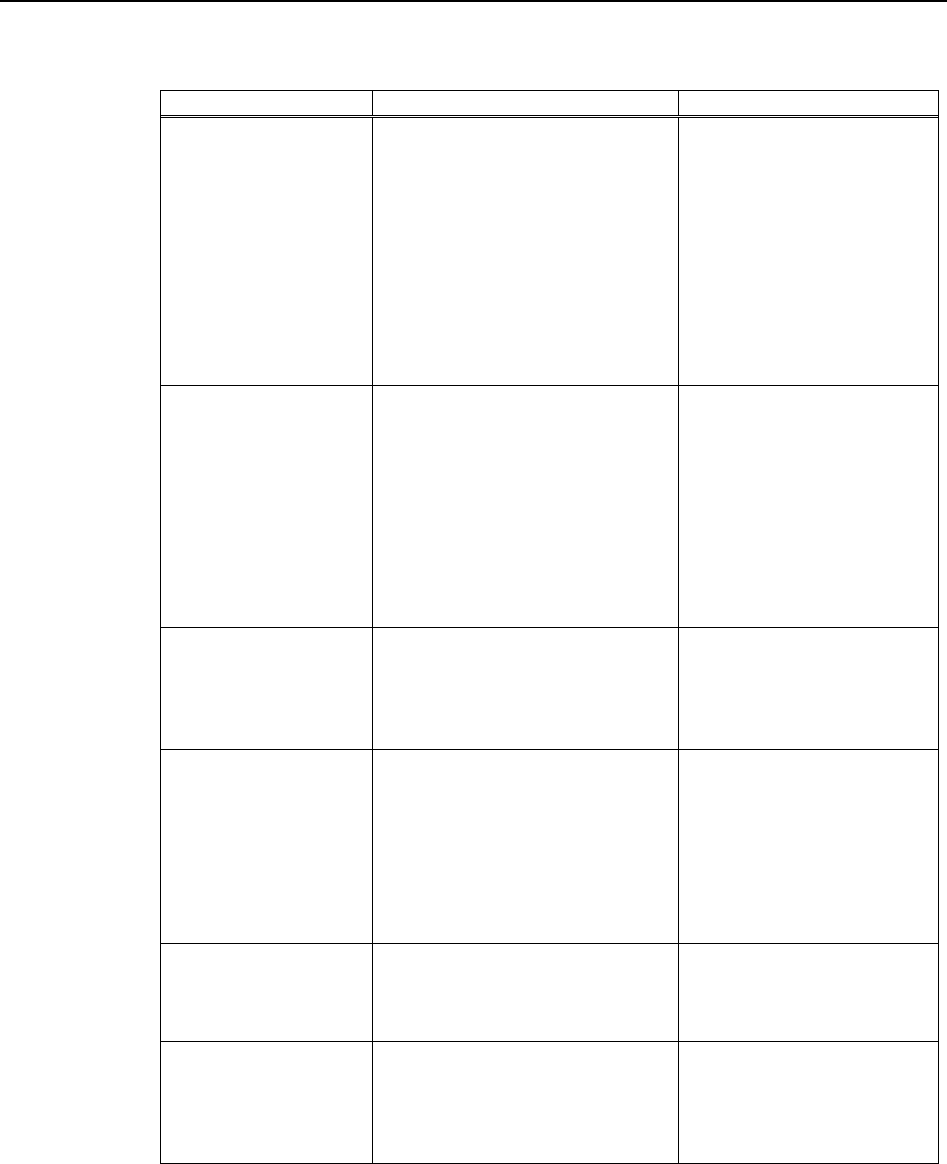
Possible Cause Examination Method Countermeasure
{ Disconnected
terminating
resistors
{ Cable
disconnection
{ Disconnected
connector
{ Disconnected
signal wire
(1) Check that terminating
resistors are connected to
both ends of the network.
(2) Measure resistance between
signal wires with device
power supply OFF.
→ Normal: 100 to 120
Ω
z Measuring point: Connection
of the trouble unit
z For detail, refer to the section
4.2.3.1 Connection Problem.
Fix the problem.
How to find the trouble
point:
Remove the terminating
resistor on one end of the
network. The trouble point
is where resistance changes
from 220
Ω.
{ Loose connector
{ Loose signal wire
Check for the connection of
connectors and signal wires.
→ The connectors and signal
wires should be firmly
connected.
z Checkpoint: all stations and all
branch taps
z For details, refer to the section
4.2.3.2 Loose Connector and
Signal Wire.
Connect the connectors and
signal wires again.
{ Electrical surges of
device power
supply
Measure voltage of device power
supply at the trouble unit.
→ It should be within the range
of sufficient voltage for device
operation.
Check voltage of the device
power supply.
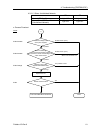
{ Noise
(external cause)
Check the noise intrusion via the
following paths (1) to (3).
(1) Noise via shield
(2) Induced noise via
communication cable
(3) Device power supply
→ For details, refer to the section
4.2.3.3 Noise Intrusion.
Take countermeasures
against noise.
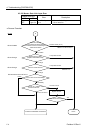
{ Broken unit Replace the trouble unit with a
new one.
→ Verify whether the problem is
fixed.
Replace the unit with a new
one.
z No cause is
identified.
Identify the trouble point by
dividing the network.
→ For details, refer to the section
4.2.3.4 Broken Unit
Examination.
118 Fieldbus I/O Rev.6