1. Introduction
1.4 EtherNet/IP
Overview of EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP is a fieldbus network that provides easy interconnection between control devices
(PLC, PC, sensor, actuator, etc.).
EtherNet/IP was developed by Allen-Bradley as an open communication standard to connect
various field devices (sensor, actuator, robot controller, etc.). Because of the open
communication standard, EtherNet/IP users can easily construct a multi-vendor system with
various devices developed around the world.
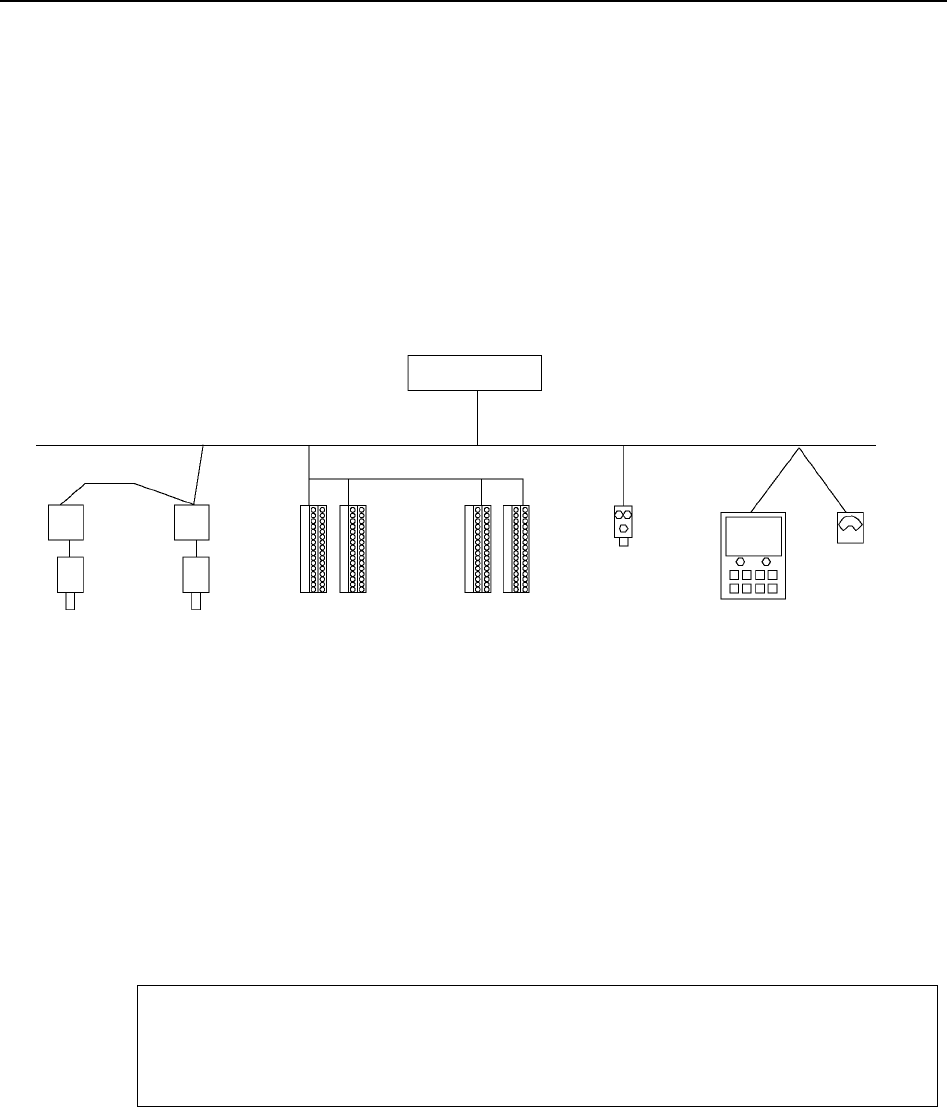
Controller
Motor Driver
from Company A
Motor Driver
from Company B
Intelligent I/O
from Company C
Intelligent I/O
from Company D
Photo Sensor
from Company E
Analog Device
from Company G
HMI Device
from Company F
Ethernet/IP Network
Features of EtherNet/IP
Reduced Wiring
Compared with parallel wiring, EtherNet/IP employs a standard Ethernet cable which
substantially reduces the number of necessary wires, wiring time and cost.
Detachable communication connectors provide you with simple wiring between nodes and
easy network separation or reconstruction.
Specified environment-resistance cables allow you to construct an environment-resistant
system at low cost.
You can use the generic Ethernet hub or Ethernet switch for the EtherNet/IP. However, be
sure to a use product complying with the industrial standards or noise resistant Ethernet
cable (STP cable). If you use an office use product or UTP cable, it may causes
communication errors and may not offer the proper performance.
)
NOTE
Open Standard (Multi-vendor)
Due to an open communication standard, various devices from many manufacturers are
available. Standardized communication connectors provide you with easy network
construction.
The maintenance spare parts stored on site (factory, etc.) can be reduced because different
manufacturers’ devices are used in case of a breakdown. Similar products are available
around the world due to a global standard EtherNet/IP.
8 Fieldbus I/O Rev.6


















