Hitachi Command Control Interface (CCI) User and Reference Guide 109
2.11 Recovery Procedures for HA Configurations
After configuring and starting Hitachi TrueCopy operations, the system administrator should
conduct operational tests for possible failures in the system. In normal operation, service
personnel obtain information for identifying the failure cause on the SVP. However, a motive
for the action above should be given by the Hitachi TrueCopy operation command.
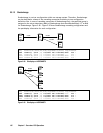
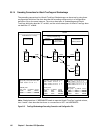
Figure 2.58 shows the system failover and recovery
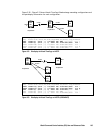
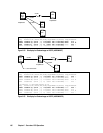
procedure. Figure 2.59 shows the
regression and Hitachi TrueCopy recovery procedure.
Pvol recovers.
Pairresync -swaps
Takeover
Takeover
Host A
Host B
P
Vol
S
Vol
Host A
Host B
S
Vol
P
Vol
cd
Host A goes down.
Host A
Host B
P
Vol
S
Vol
Host A
Host B
P
Vol
Svol
SSUS
(SSWS)
Host A
Host B
S
Vol
P
Vol
cde
Difference
Pvol goes down.
Mirror state
Takeover state
Recovery state
c A failure occurs in the host A server (1-top) or in the Pvol (1-bottom).
d Host B detects the failure of host A or the Pvol and issues a takeover command to make the SVOL usable. Host B takes over
processing from host A. In the case of host A failure (1-top), the Swap-takeover command will be executed. In the case of
Pvol failure (1-bottom), the SVOL-SSUS-takeover command will be executed.
e While host B continues processing, PVOL and SVOL are swapped (pairresync -swaps), and the delta data (BITMAP)
updated by host B is fed back to host A.
f After host A or the Pvol has recovered, host A can take over processing from host B by executing the swap-takeover
(horctakeover) command.
Figure 2.58 System Failover and Recovery