40 Chapter 2 Overview of CCI Operations
2.7 Overview of CCI Data Protection Operations
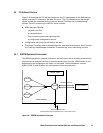
User data files are normally placed to a disk through some software layer such as file
system, LVM, diskdriver, SCSI protocol driver, bus adapter, and SAN switching fabric. Data
corruption can happen on above software bugs and human error as follows. The purpose of
Data Protection is to prevent writing to volumes by RAID storage system guarding the
volume.
The CCI Data Protection functions include:
Database Validator (sections 2.7.1, 2.7.2). For further information on Database
Validator, please refer to the Database Validator Reference Guide for the storage
system.
Data Retention Utility (DRU) (called “Open LDEV Guard” on 9900V/9900) (sections 2.7.3
and 2.7.4). For further information on Data Retention Utility, please re
fer to the Data
Retention Utility User’s Guide for USP V/VM and USP/NSC (Open LDEV Guard User’s
Guide for Lightning 9900V and 9900).
2.7.1 Database Validator
The purpose of Database Validator (9900V and later) is to prevent data corruption by
checking Oracle data validation before ORACLE data block is written on a disk.
Data Block corruption: Oracle data is corrupted by some intervening software layer and
hardware components. The RAID storage system can check the validity of the data block
before the Oracle DataBlock is written to disk.
Data Block address corruption: The OS (file system, LVM, Diskdriver) may write blocks
to the wrong location. The RAID storage system can check the validity of the data block
address to verify that the Oracle DataBlock is written to the correct location on disk.
Protection of Oracle volume: Oracle datafiles might be overwritten by a non-Oracle
application or by human operation using a command. The RAID storage system can
protect volumes storing Oracle files to prevent the volumes from being modified by
another application or by human error.
Note: For information on error monitoring for Database Validator, see section 2.10.2.