Hitachi Command Control Interface (CCI) User and Reference Guide 201
statu
s
SVOL_E Æ 5,6
never SVOL_E Æ 5,6
PDUB
async SVOL Æ 5,6
21 S-VOL EX_EVOLCE
EX_EVOLCE
22 COPY Unknown SVOL_E * Æ 4,5
SVOL_E*
data SVOL Æ 4
status SVOL Æ 4
never SVOL_E Æ 4
23 PAIR/
PFUL
async
SVOL Æ 4
PSUS SVOL_E Æ 4 24
PFUS
SVOL Æ 4-1
data SVOL Æ 5,6
status SVOL_E Æ 5,6
never SVOL_E Æ 5,6
25 PSUE
PDUB
async
EX_ENORMT or
EX_CMDIOE
YYY
SVOL Æ 5,6
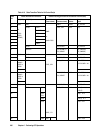
Explanation of terms in Table 4.16:
XXX = Pair status of P-VOL returned by “pairvolchk -s” or “pairvolchk -s -c” command
YYY = Pair status of S-VOL returned by “pairvolchk -s” or “pairvolchk -s -c” command
PAIR STATUS = Since the P-VOL controls status, PAIR STATUS is reported as PVOL_XXX
(except when the P-VOL’s status is Unknown).
PVOL-PSUE = PVOL-PSUE-takeover
PVOL-SMPL = PVOL-SMPL-takeover
Nop = Nop-takeover
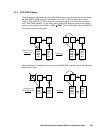
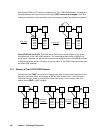
Swap = Swap-takeover. When the horctakeover command execution succeeds, the state
transitions to the indicated (
Æ) state number.
SVOL
= SVOL-SSUS takeover or Swap-takeover. In case of a host failure, this function
executes Swap-takeover. In case of an ESCON/fibre-channel or P-VOL site failure, this
function executes SVOL-SSUS-takeover.
SVOL_E
= Execute SVOL-SSUS takeover and return EX_VOLCUR.
SVOL_E*
= Return EX_VOLCUR.
When the horctakeover command execution succeeds, the state transitions to the
indicated (
Æ) state number. For example, if the HA control script sees SVOL_PAIR at the
local (near) volume and PVOL_PAIR at the remote (far) volume (like state 16 above), it
will perform a swap takeover which will result in a state 12 situation.