Hints and Tips 217
bootinfo -p, you will get different results for PReP and CHRP/RPA machines.
The result of
bootinfo -T is always rspc for every PCI-based machine.
The results of
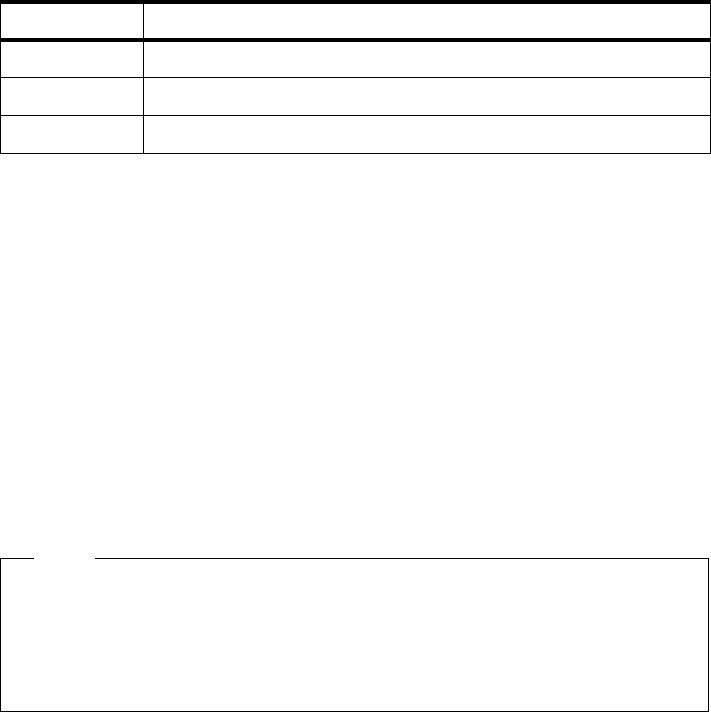
bootinfo with the -p option are shown in Table 40.
Table 40. Results of bootinfo -p
8.3.2 Creating a System Backup
Creating a system backup, or mksysb, is very simple. If you were using a tape
drive, for example
rmt0, you could easily create a system backup from the
command line by typing:
# mksysb -i /dev/rmt0
This would create a bootable image of your system that can be used to either
re-create the system or to restore files.
Alternatively, you can use SMIT to create your system image. To do this, you
can use the SMIT fastpath:
# smit mksysb
8.3.3 Restoring Your System Backup
You can restore your mksysb by booting from the tape that you have created
and following the instructions that are displayed. To boot from the tape, you
have to press F1 (or 1 on an ASCII terminal) during the firmware boot, and
select the tape device to boot from. Alternatively, you can place the tape drive
as the first device in the customized boot list so that the tape will
automatically boot when the machine is powered-on or rebooted.
Platform Description
chrp CHRP-compliant PCI-based RS/6000 machines
rspc PReP-compliant PCI-based RS/6000 machines
rs6k Micro Channel-based RS/6000 machines
Creating a system backup with the mksysb command only saves data in the
rootvg volume group. If you want to also save data from a non-root volume
group you have to use the
savevg command or the SMIT fastpath:
# smit savevg
Note


















