Overview
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 15
Datasheet Volume One of Two
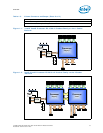
• Independent channel mode or lockstep mode
• Data burst length of eight cycles for all memory organization modes
• Memory DDR3 data transfer rates of 800, 1066, 1333, 1600, and 1866 MT/s
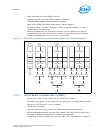
• 64-bit wide channels plus 8-bits of ECC support for each channel
• DDR3 standard I/O Voltage of 1.5 V and DDR3 Low Voltage of 1.35 V
• 1-GB, 2-GB, and 4-GB DDR3 DRAM technologies supported for these devices:
— UDIMMs x8, x16
— RDIMMs x4, x8
— LRDIMM x4, x8 (2-Gb and 4-Gb only) LR-DIMMs are supported only on server
specific SKUs (Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product
families). LR-DIMMs are not supported in workstation specific SKUs such as the
Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2 product family.
• Up to 8 ranks supported per memory channel: 1, 2 or 4 ranks per DIMM
• Open with adaptive idle page close timer or closed page policy
• Per channel memory test and initialization engine can initialize DRAM to all logical
zeros with valid ECC (with or without data scrambler) or a predefined test pattern
• Isochronous access support is not available on any CPU model containing two home
agents.
• Minimum memory configuration: independent channel support with 1 DIMM
populated
• Integrated dual SMBus master controllers
• Command launch modes of 1n/2n
• RAS Support (including and not limited to):
Note: RAS support depends on processor SKU. For example, Workstation SKUs do
not support sparing or tagging, lockstep mode, mirroring mode, channel
mirroring mode within a socket, error containment.
— Rank Level Sparing and Device Tagging
— Demand and Patrol Scrubbing
— DRAM Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for any single x4 or x8 DRAM
device failure. Independent channel mode supports x4 SDDC. x8 SDDC
requires lockstep mode
— Lockstep mode where channels 0 & 1 and channels 2 & 3 are operated in
lockstep mode
— The combination of memory channel pair lockstep and memory mirroring is not
supported
— Data scrambling with address to ease detection of write errors to an incorrect
address.
— Error reporting via Machine Check Architecture
— Read Retry during CRC error handling checks by iMC
— Channel mirroring within a socket
— Channel Mirroring mode is supported on memory channels 0 & 1 and channels
2 & 3
— Error Containment Recovery
• Improved Thermal Throttling with dynamic Closed Loop Thermal Throttling (CLTT)