DEFINITY Enterprise Communications Server Release 8.2
Overview
555-233-002
Issue 1
April 2000
Private Networking Features
111
QSIG
DCS Over ISDN-PRI D-channel
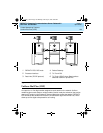
Enhances DCS by allowing access to the public network for DCS connections between
DCS switch nodes. With this feature (also known as DCS+), DCS features are no longer
restricted to private facilities. The ISDN-PRI B-channel is used for voice communications,
and the ISDN-PRI D-channel is used to transport DCS control information.
QSIG
QSIG provides compliance to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
ISDN-PRI private-networking specifications. QSIG is defined by ISO as the worldwide
standard for private networks. QSIG features are supported on BRI trunks.
QSIG is the generic name for a family of signaling protocols. The Q-reference point or
interface is the logical point where signaling is passed between 2 peer entities in a private
network. QSIG signaling can provide feature transparency in a single-vendor or
multi-vendor environment.
QSIG provides call-related Supplementary Services. These are services that go beyond
voice or data connectivity and number transport and display. Examples of Supplementary
Services include Name Identification, Call Forwarding (Diversion), and Call Transfer.
Call Completion
Call Completion utilizes the QSIG Platform enhancement Call Independent Signaling
Connections and is functionally equivalent to the Distributed Communications System
(DCS) feature: AutoCallback.
Call Independent Signaling Connections
(CISC)
Call Independent Signaling Connections (CISC) are used to pass QSIG Supplementary
Service information that is independent of an active call between two QSIG compliant
nodes. Implementation is based on the ISO standard for CISC. It is possible to determine
the status of a QSIG TSC by using the "status Signaling group" command on the SAT.
233002_1.book Page 111 Monday, February 21, 2000 8:28 AM