EDS-508 Series User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-23
STP and the protocol features supported by your EDS.
NOTE
The protocol is part of the IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition bridge specification. The following
explanation of STP uses bridge instead of switch.
What is STP?
STP (802.1D) is a bridge-based system that allows you to implement parallel paths for network
traffic and uses a loop-detection process to:
# Find and disable the less efficient paths (that is, the paths that have a lower bandwidth).
# Enable one of the less efficient paths if the most efficient path fails.
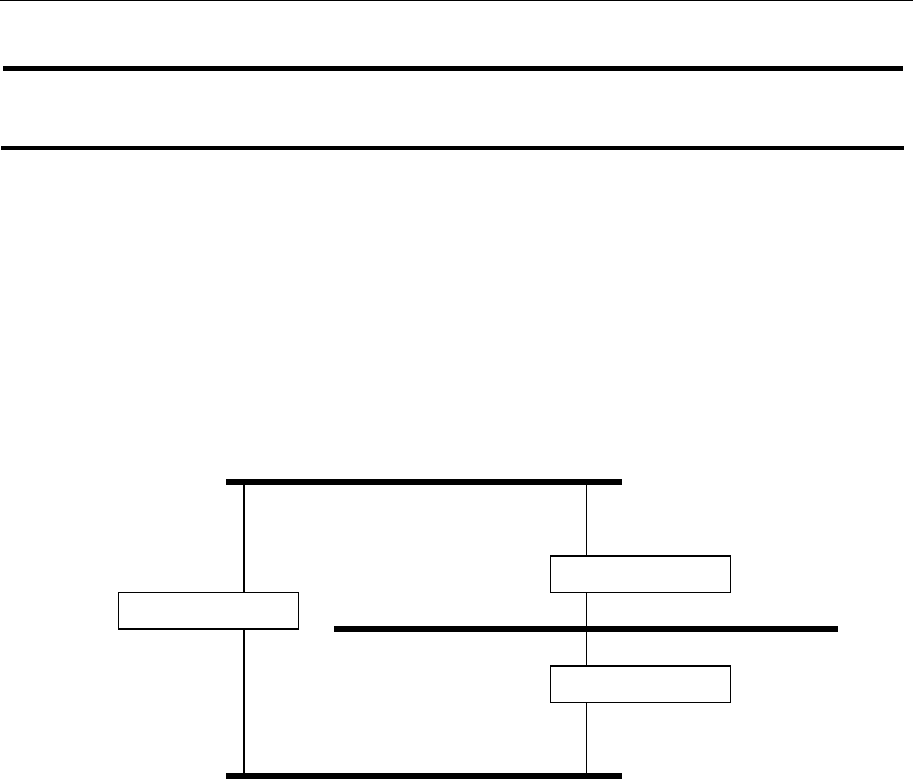
As an example, the figure below shows a network containing three LAN segments separated by
three bridges. With this configuration, each segment uses at most two paths to communicate with
the other segments. If STP is NOT enabled, this configuration creates loops that cause the network
to overload.
The next figure shows the result of enabling STP on the bridges in the configuration. STP detects
duplicate paths and prevents, or blocks, one of them from forwarding traffic, so that the
configuration will work satisfactorily. STP could have determined, for example, that traffic from
LAN segment 2 to LAN segment 1 should flow through Bridges C and A because this path has a
greater bandwidth and is therefore more efficient.
Brid
g
e B
Brid
g
e C
LAN 1
LAN 2
LAN 3
Brid
g
e A


















