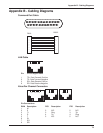
80
Glossary
A
Access: The T1 line element made up of two pairs of wire that the telephone company brings to the customer premises. The Access portion
ends with a connection at the local telco (LEC or RBOC).
Accunet Spectrum of Digital Services (ASDS): The AT&T 56K bps leased (private) line service. Similar to services of MCI and Sprint.
ASDS is available in nx56/64K bps, where n=1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12.
ACK (ACKnowledgement code) (pronounced "ack"): A communications code sent from a receiving modem to a transmitting modem to
indicate that it is ready to accept data. It is also used to acknowledge the error-free receipt of transmitted data. Contrast with NAK.
Adaptive Differential Pulse Code (ADCPM): In multimedia applications, a technique in which pulse code modulation samples are com-
pressed before they are stored on a disk. ADCPM, an extension of the PCM format, is a standard encoding format for storing audio informa-
tion in a digital format. It reduced storage requirements by storing differences between successive digital samples rather than full values.
Address: A numbered location inside a computer. It is how the computer accesses its resources, like a video card, serial ports, memory, etc.
AMI line coding: One of two common methods of T1 line coding (with B8ZS). AMI line coding places restrictions on user data (B8ZS does
not).
Analog signal: A waveform which has amplitude, frequency and phase, and which takes on a range of values between its maximum and
minimum points.
Analog Transmission: One of two types of telecommunications which uses an analog signal as a carrier of voice, data, and video. An
analog signal becomes a carrier when it is modulated by altering its phase, amplitude, and frequency to correspond with the source signal.
Compare with digital transmission.
Application Program Interface (API): A software module created to allow dissimilar, or incompatible applications programs to transfer
information over a communications link. APIs may be simple or complex; they are commonly required to link PC applications with mainframe
programs.
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) (pronounced "askey"): A binary code for data that is used in communica-
tions and in many computers and terminals. The code is used to represent numbers, letters, punctuation and control characters. The basic
ASCII code is a 7-bit character set which defines 128 possible characters. The extended ASCII file provides 255 characters.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): A very high-speed method of transmission that uses fixed-size cells of 53 bytes to transfer informa-
tion over fiber; also known as cell relay.
AT Commands: A standard set of commands used to configure various modem parameters, establish connections and disconnect. The
"AT" is used to get the "attention" of the modem before the actual command is issued.
Availability: The measure of the time during which a circuit is ready for use; the complement of circuit "outage" (100% minus % outage = %
available).
B
B7ZS (Bipolar 7 Zero Suppression) line coding: One method of T1 line coding (see also "B8ZS" and "AMI"). B7ZS line coding does not
place restrictions on user data (AMI does).
B8ZS (Bipolar 8 Zero Suppression) line coding: One of two common methods of T1 line coding (with AMI). B8ZS line coding does not
place restrictions on user data (AMI does). A coding method used to produce 64K bps "clear" transmission. See also "B7ZS" and "AMI" line
coding.
Backbone: 1) A set of nodes and their interconnecting links providing the primary data path across a network. 2) In a local area network
multiple-bridge ring configuration, a high-speed link to which the rings are connected by means of bridges. A backbone may be configured as
a bus or as a ring. 3) In a wide area network, a high-speed link to which nodes or data switching exchanges (DSEs) are connected. 4) A
common distibution core that provides all electrical power, gases, chemicals, and other services to the sectors of an automated wager
processing system.
Background: An activity that takes place in the PC while you are running another application. In other words, the active user interface does
not correspond to the 'background' task.
Bandwidth: The transmission capacity of a computer channel, communications line or bus. It is expressed in cycles per second (hertz), the
bandwidth being the difference between the lowest and highest frequencies transmitted. The range of usable frequencies that a transmission
medium will pass without unacceptable attenuation or distortion. Bandwidth is a factor in determining the amount of information and the
speed at which a medium can transmit data or other information.
Backward Explicit Congestion Notification (BECN): A bit that tells you that a certain frame on a particular logical connection has encoun-
tered heavy traffic. The bit provides notification that congestion-avoidance procedures should be initiated in the opposite direction of the
received frame. See also FECN (Forward Explicit Congestion Notification).
Basic Rate Interface (BRI): An ISDN access interface type comprised of two B-channels each at 64K bps and one D-channel at 64K bps
(2B+D).