C
ONFIGURING
THE
S
WITCH
3-282
Displaying Statistics for IP Protocols
IP Statistics
The Internet Protocol (IP) provides a mechanism for transmitting blocks
of data (often called packets or frames) from a source to a destination,
where these network devices (i.e., hosts) are identified by fixed length
addresses. The Internet Protocol also provides for fragmentation and
reassembly of long packets, if necessary, for transmission through “small
packet” networks.
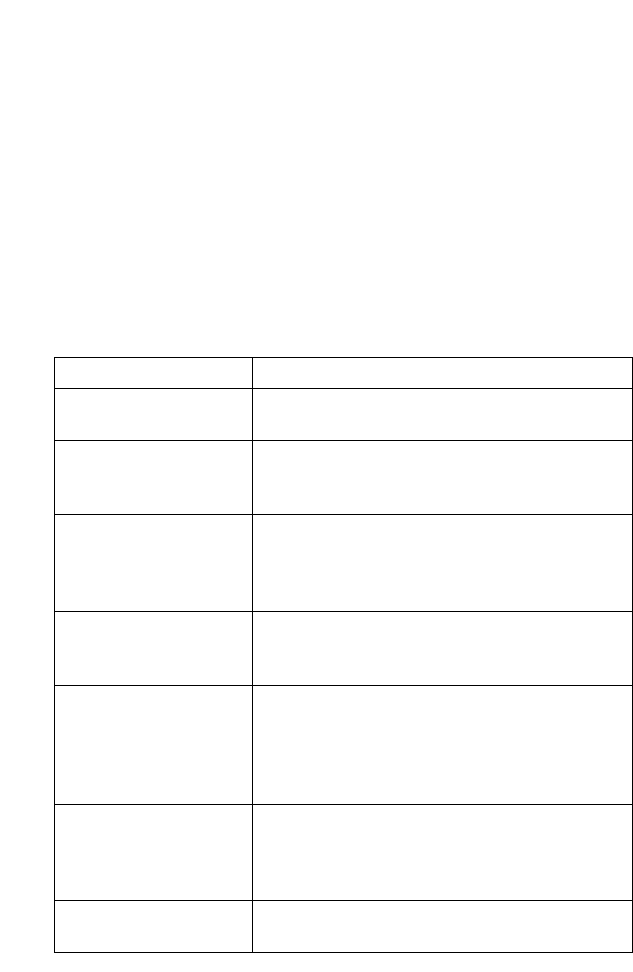
Table 3-18 IP Statistics
Parameter Description
Packets Received The total number of input datagrams received from
interfaces, including those received in error.
Received Address Errors The number of input datagrams discarded because the
IP address in the header's destination field was not a
valid address for this entity.
Received Packets
Discarded
The number of input datagrams for which no
problems were encountered to prevent their
continued processing, but which were discarded (e.g.,
for lack of buffer space).
Output Requests The total number of datagrams which local IP
user-protocols (including ICMP) supplied to IP in
requests for transmission.
Output Packet No Route The number of datagrams discarded because no route
could be found to transmit them to their destination.
Note that this includes any datagrams which a host
cannot route because all of its default gateways are
down.
Datagrams Forwarded The number of input datagrams for which this entity
was not their final IP destination, as a result of which
an attempt was made to find a route to forward them
to that final destination.
Reassembly Required The number of IP fragments received which needed
to be reassembled at this entity.


















