23
In order to determine the drive’s actual output frequency, the data contained in the
output frequency word (offsets 2 and 3) must first be converted from hexadecimal to
decimal, and then divided by 100. For example, if the output frequency high byte is
0x12 and the output frequency low byte is 0x34, then 0x1234 converted to decimal is
4660. Dividing this number by 100, the actual operating frequency of 46.60Hz is
obtained.
In this way, network data values of 0x0000 ∼ 0x9C40 correspond to the G3’s actual
allowable output frequency range of 0.00Hz ∼ 400.00Hz.
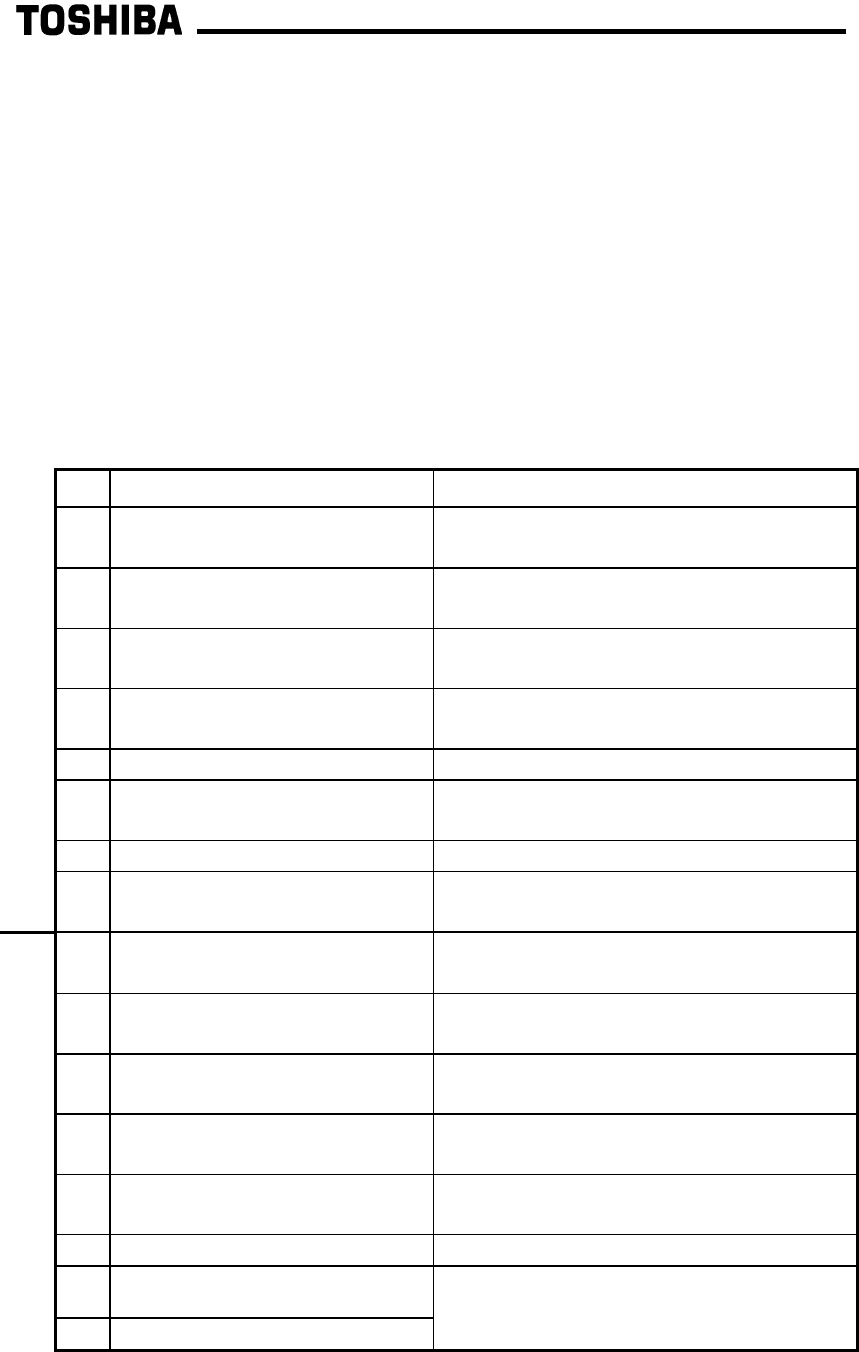
Table 2 : Status Word Format
Bit Function Value
0 Run / stop status 0: Stopped
1: Running
1 Run enable status 0: Run enabled
1: Stopped
2 Forward / reverse status 0: Reverse
1: Forward
3 Accel / decel #1 / #2 selection
status
0: Accel / decel #1
1: Accel / decel #2
4 Reserved Always “0”
5 Fault status 0: Faulted
1: Not Faulted
6 Reserved Always “0”
Low Byte
7 Jog mode status 0: Normal (accel/decel mode)
1: Jog mode
8 Feedback enable status 0: Feedback invalid
1: Feedback valid
9 Compulsory DC injection
braking mode
0: DC injection braking inactive
1: DC injection braking active
A Fundamental parameter
switching
0: V/F #1
1: V/F #2
B Coast stop command status 0: Normal
1: Coast to stop
C Emergency off command 0: Normal
1: Emergency off
D Reserved Always “0”
E
Main Circuit Undervoltage 0: Normal
1: Undervoltage
High Byte
F Reserved Always “0”


















