P-334U/P-335U User’s Guide
Chapter 4 Wireless LAN 69
For wireless networks, there are two typical places to store the user names and passwords for
each user.
• In the AP: this feature is called a local user database or a local database.
• In a RADIUS server: this is a server used in businesses more than in homes.
If your AP does not provide a local user database and if you do not have a RADIUS server,
you cannot set up user names and passwords for your users.
Unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network, even if
they cannot use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless
users to get a valid user name and password. Then, they can use that user name and password
to use the wireless network.
Local user databases also have an additional limitation that is explained in the next section.
4.2.4 Encryption
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless
network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot
understand the message.
The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of user authentication. (See
Section 4.2.3 on page 68 for information about this.)
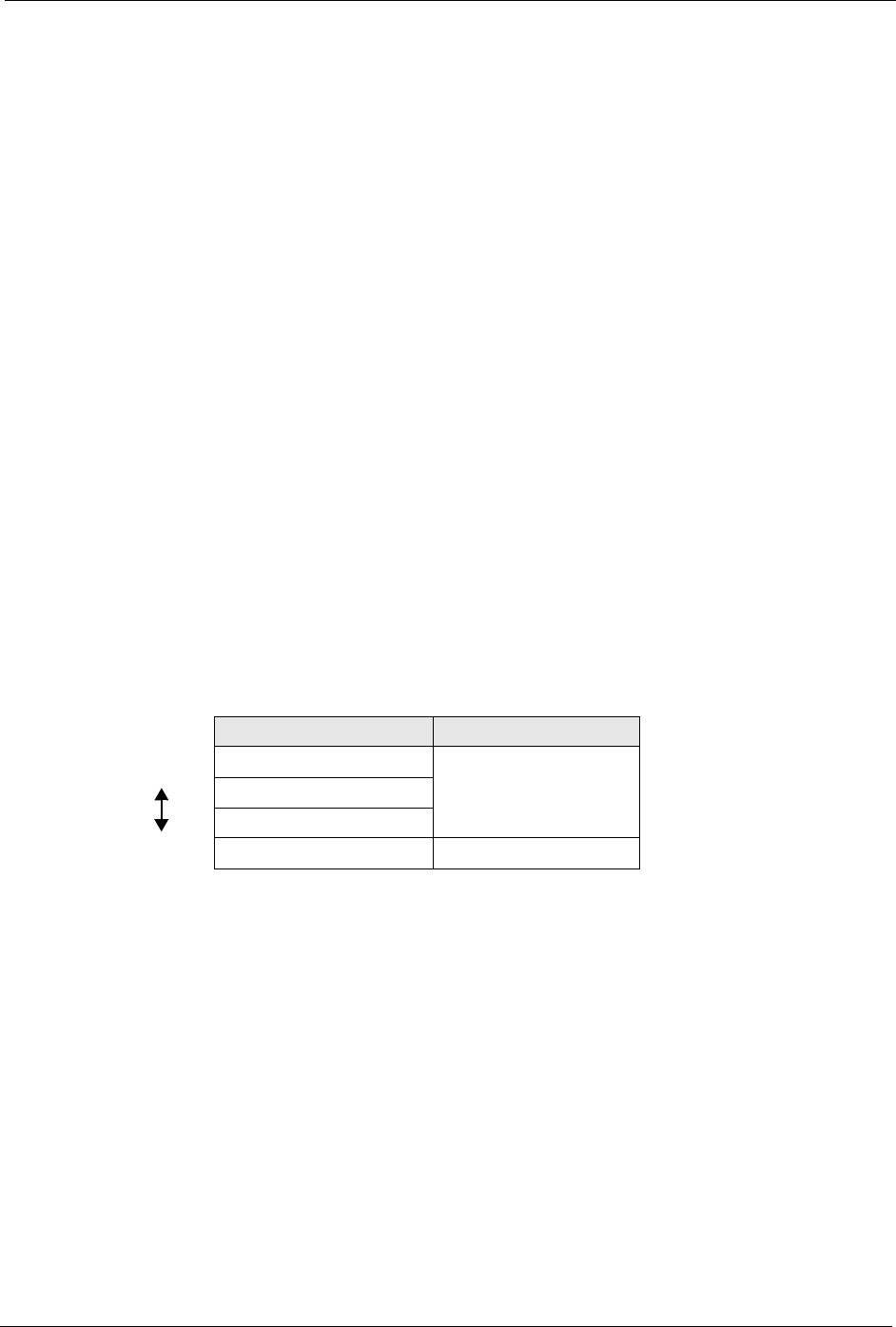
Table 22 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
No Authentication RADIUS Server
Weakest No Security
WPA
Static WEP
WPA-PSK
Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2
For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA or WPA2. If
users do not log in to the wireless network, you can choose no encryption, Static WEP, WPA-
PSK, or WPA2-PSK.
Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every wireless client in the wireless
network supports. For example, suppose the AP does not have a local user database, and you
do not have a RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no user authentication. Suppose the wireless
network has two wireless clients. Device A only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP
and WPA. Therefore, you should set up Static WEP in the wireless network.


















