Configuring the Switch
3-118
3
ports, and disables all other ports. Network packets are therefore only forwarded
between root ports and designated ports, eliminating any possible network loops.
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello
BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the Root Bridge. If a bridge
does not get a Hello BPDU after a predefined interval (Maximum Age), the bridge
assumes that the link to the Root Bridge is down. This bridge will then initiate
negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the network to reestablish a valid
network topology.
RSTP – RSTP is designed as a general replacement for the slower, legacy STP.
RSTP is also incorporated into MSTP. RSTP achieves must faster reconfiguration
(i.e., around 1 to 3 seconds, compared to 30 seconds or more for STP) by reducing
the number of state changes before active ports start learning, predefining an
alternate route that can be used when a node or port fails, and retaining the
forwarding database for ports insensitive to changes in the tree structure when
reconfiguration occurs.
MSTP – When using STP or RSTP, it may be difficult to maintain a stable path
between all VLAN members. Frequent changes in the tree structure can easily
isolate some of the group members. MSTP (which is based on RSTP for fast
convergence) is designed to support independent spanning trees based on VLAN
groups. Using multiple spanning trees can provide multiple forwarding paths and
enable load balancing. One or more VLANs can be grouped into a Multiple Spanning
Tree Instance (MSTI). MSTP builds a separate Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) for
each instance to maintain connectivity among each of the assigned VLAN groups.
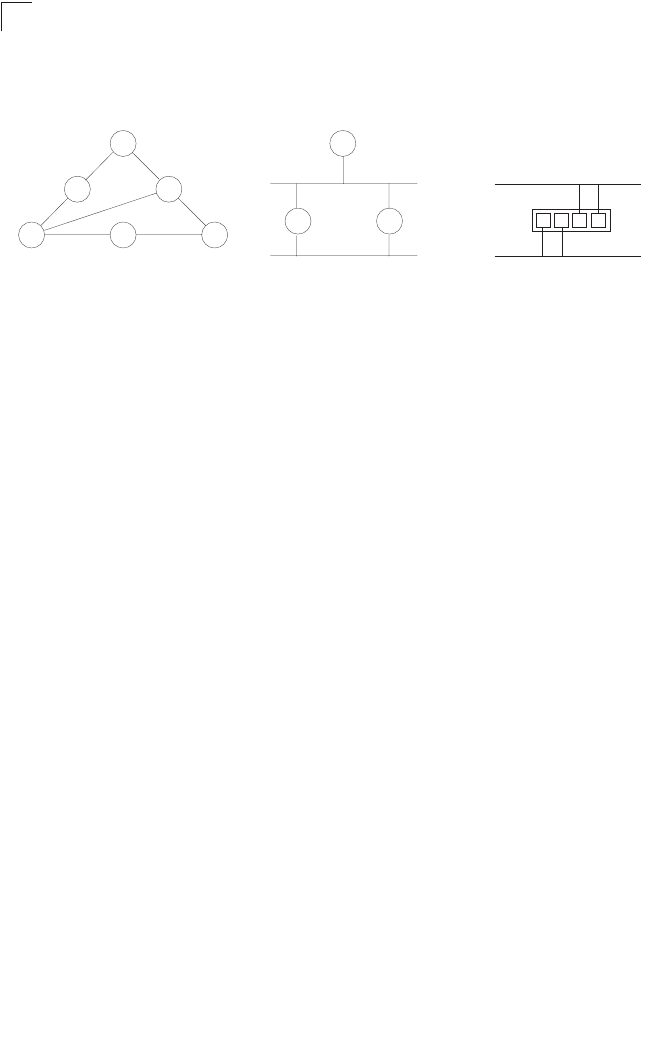
x
Designated
Root
Designated
Port
Designated
Bridge
x x
x
Root
Port
x


















