2
Bosch Security Systems | 04-2003 | 3922 988 43318 en
Digital Congress Network | Installation and Operating Manual | Chapter 11 - System Set-up and Operation
en | 11-15
Interpretation
11.9 Interpretation
The interpreter desk has two functional modes: the operational mode and the programming mode. In
the operational mode the interpreter desk is divided into two main working sections: the listening
section and the speech section. The listening section at the left side of the unit includes headphone
and loudspeaker monitoring facilities for listening to the floor or other translations. The speech section
at the right of the unit includes controls for the outgoing translation channels. In its programming
mode, operational functions can be set before a conference begins. The programming mode under a
menu driven display enables audio channels to be assigned to specific languages, the selection of the
interpreters A and B output translations, as well as providing an override and interlock facility
between and within booths.
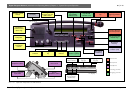
11.9.1 Incoming channel control (LISTENING)
Each interpreter desk includes a Relay select rotary switch for selection of the incoming language, as
well as three incoming channel pre-select keys a, b, and c. The pre-select keys a, b, and c can be
assigned to the interpreters three most familiar or working languages. The incoming language is
displayed on the units alphanumeric LC-display together with a quality indication, providing the
interpreter with an at a glance indication of the quality of the incoming language. For example the
quality indication displays whether the incoming language is direct from the floor speaker (FLOOR) or
whether its a translation of the floor language (+) or whether its a translation of a translation of the
floor language (-). Monitoring the incoming languages is done via the units built-in loudspeaker (floor
only) or by using headphones or headset. Three rotary controls at the lower left of the unit provide
headphone volume, treble and bass adjustment. A rotary switch at the top left of the unit provides a
loudspeaker volume control adjustment.
11.9.2 Outgoing channel control (SPEAKING)
To distribute the translation, the desk provides two outputs, output A and output B. Output A is a
preset output used for the interpreter’s normal outgoing output, and output B (if selected during
programming) is used for translating from less common languages, or as a second outgoing language
output where different languages are to be distributed from the same desk.
Selection of the A or B outputs is by means of two push-buttons marked A and B. Red LEDs adjacent
to the push-buttons indicate which output has been selected. If output B is selected, the output
language from that desk can be automatically distributed to the other interpreter desk (booths) for
relay interpretation into other languages (if the auto-relay function is enabled in the desk
programming procedure).
11.9.3 Microphone (Micro)
A microphone on/off switch (Micro) controls the status of the units microphone while a Mute push-
button temporarily mutes the microphone for as long as the key remains pressed. An illuminated light
ring and a microphone status indicator (LED bar) indicates microphone on status.
11.9.4 Microphone locks
In its programming mode, the desk can be programmed with a microphone ‘Override’ or microphone
‘Interlock’ function, or given free microphone access ‘None’. The microphone interlocks are only
active when interpreter desks from different booths, try to gain access to the same channel.
11.9.5 ‘Override’
If programmed, the ‘Override’ function allows all interpreters assigned to the same output channel, to
switch-on their microphones and access the output channel on a First-In-First-Out basis - thus
switching off already active microphones. This function therefore, assures that only one microphone at
a time is active on a channel.
‘Interlock’
The interlock function permits only one microphone on a channel to be switched on at any time, thus
preventing other interpreters from using the same output channel. The ‘Interlock’ function therefore
operates on a First-In-First-Served basis.
‘None’
When programmed ‘None’, interpreters assigned to the same channel can switch on their
microphones simultaneously.
NOTE: In PC-based systems the ‘Override’, ‘Interlock’ and ‘None’ facility can be pro-
grammed for within booths or between booths. In stand-alone systems the ‘Override’,
‘Interlock’ and ‘None’ facilities are only active between booths.
11.9.6 Relay Interpretation with auto-relay
In circumstances where the original floor-language is ‘well known’ or not ‘so well known’, two different
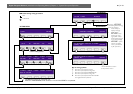
operational procedures can be used. In normal operational mode (FIG 11-9) the original floor
language is well-known to all interpreters, and they listen to the original floor language for
interpretation. The translations are then fed to the language distribution channels. In situations where
interpreters are unfamiliar with the floor language and therefore unable to interpret it, the system
offers an automated relay interpretation facility (auto-relay - see FIG 11-10). An interpreter assigned
to translate the floor language, translates it into another language easily understood by other
interpreters. The floor language on all interpreter desks will be replaced by this transfer interpretation.
This transfer interpretation or “auto-relay” is then used as the base for further translations.
In the example shown in FIG 11-10, Japanese is the floor and the auto-relay facility is enabled on the
Japanese interpreter’s desk. This interpreter selects outgoing channel B and automatically relays an
English interpretation as AUTO-RELAY to all other desks for interpretation and also feeds the English
language distribution channel. The incoming channel AUTO-RELAY indicator shows on all other desks
that auto-relay is active.