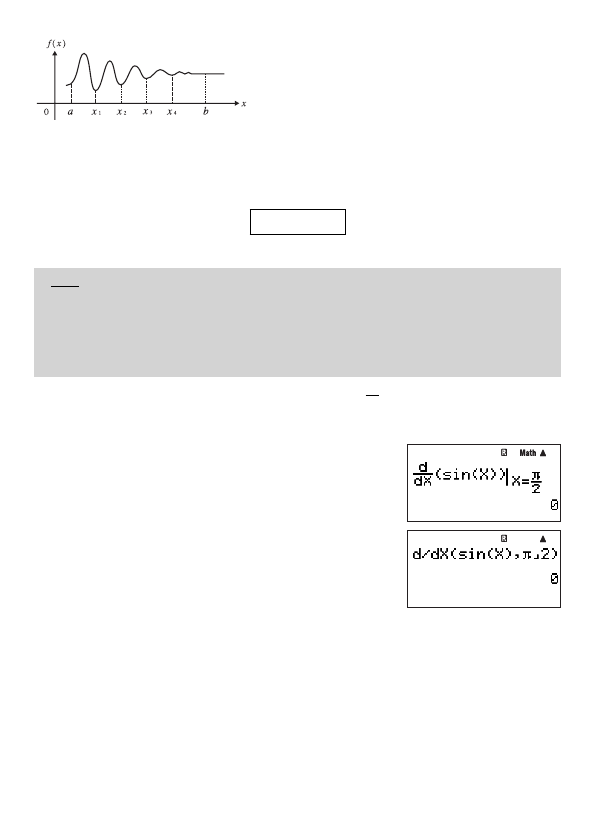
E-45
a
b
f(x)dx =
a
x
1
f(x)dx +
x1
x
2
f(x)dx +
.....+
x4
b
f(x)dx
∫∫∫
∫
k
Derivative
Your calculator performs differential calculations by approximating the derivative based on
centered difference approximation. Calculation is performed using the function shown below.
d
/
dx
(
A
Syntax and Input
d
/
dx
(
f
(
x
),
a
,
tol
)
f
(
x
): Function of
x
(Input the function used by variable X.)
• All variables other than X are viewed as constants.
a
: Value of point (derivative point) of desired derivative coeffi cient
tol
: Error tolerance range (Can be input only when linear display is being used.)
• This parameter can be omitted. In that case, a tolerance of 1 × 10
–10
is used.
Example: To obtain the differential coeffi cient at point
x
=
π
2
for the function
y
= sin(
x
)
(
tol
value not input)
V
z
– {MATH}
2
(d/dX)
s
S
0
(X)
)
.....
1
B
(Continuing from
1
, above)
e
'
1
Z
(
π
)
c
2
E
b
(Continuing from
1
, above)
,
1
Z
(
π
)
'
2)
E
A
Remarks
• Use of
d
/
dx
( is supported in the COMP, SD, REG, and EQN Modes only.
• The following functions cannot be input for the
f
(
x
),
a
, and
tol
parameters:
∫
(,
d
/
dx
(,
d
2
/
dx
2
(,
Σ
(. In addition, the Pol( and Rec( functions, and the random number functions cannot be
input for the
f
(
x
) parameter.
• In the case of differentiation of a trigonometric function, select Rad for the angle unit.
• Specifying a smaller value for the
tol
parameter tends to improve precision, but it also
causes the calculation to take more time. Specify a
tol
value greater than 1 × 10
–14
.
• You will not be able to input a
tol
value while using natural display.
• Non-consecutive points, abrupt fl uctuation, extremely large or small points, infl ection
points, and the inclusion of points that cannot be differentiated, or a differential point or


















