E-62
k
Performing Matrix Calculations
This section presents a number of actual examples of matrix calculations.
• Before performing matrix calculations, you need to perform the procedure under “Inputting
and Editing Matrix Data” (page 59) to input data into the matrices you plan to use in the
calculations.
• The table below shows the matrix name notation used in this section. When you see a
matrix name in a procedure, you need to perform one of the key operations shown below.
When you see this matrix name: Perform this key operation:
Mat A
z
– {MATRIX}
2
(Mat)
S
0
(A)
Mat B
z
– {MATRIX}
2
(Mat)
S
'
(B)
Mat C
z
– {MATRIX}
2
(Mat)
S
$
(C)
• All of the examples in this section are performed using natural display.
A
Adding and Subtracting Matrices
You can add or subtract matrices only if their dimensions are identical.
Example:
2 0
0 2
+
1 2
3 4
This example assumes that Mat A contains
2 0
0 2
and Mat B contains
1 2
3 4
.
Mat A
+
Mat B
E
A
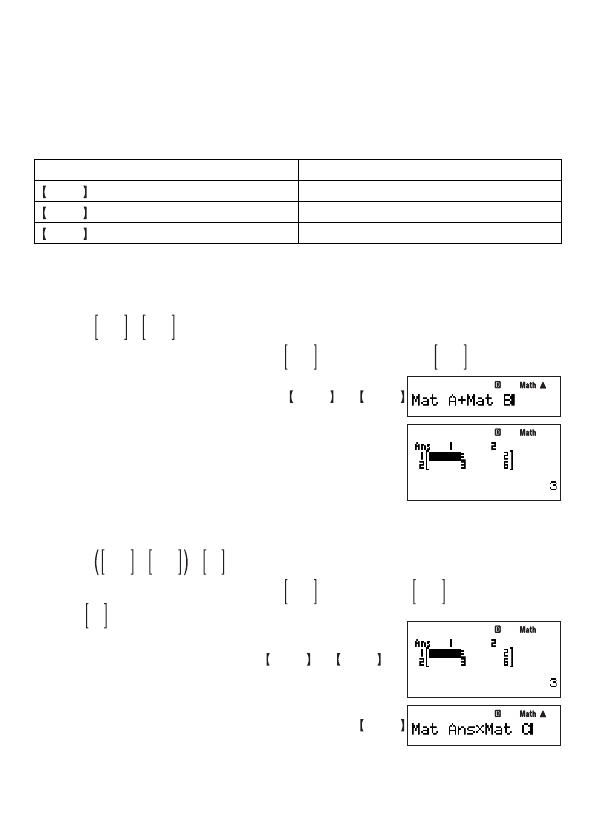
Multiplying Matrices
You can multiply two matrices only if they both have the same number of rows.
Example:
2 0
0 2
+
1 2
3 4
×
3
5
This example assumes that Mat A contains
2 0
0 2
, Mat B contains
1 2
3 4
, and Mat C
contains
3
5
.
Mat A
+
Mat B
E
*
Mat C