2-45
S Matrix Arithmetic Operations [OPTN]-[MAT]-[Mat]/[Iden]
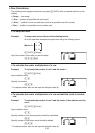
Example 1 To add the following two matrices (Matrix A + Matrix B):
*(MAT)(Mat)?T(A)
(Mat)?J(B)U
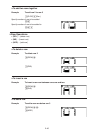
Example 2 To multiply the two matrices in Example 1 (Matrix A s Matrix B)
*(MAT)(Mat)?T(A)
(Mat)?J(B)U
• The two matrices must have the same dimensions in order to be added or subtracted. An
error occurs if you try to add or subtract matrices of different dimensions.
• For multiplication (Matrix 1 s Matrix 2), the number of columns in Matrix 1 must match the
number of rows in Matrix 2. Otherwise, an error occurs.
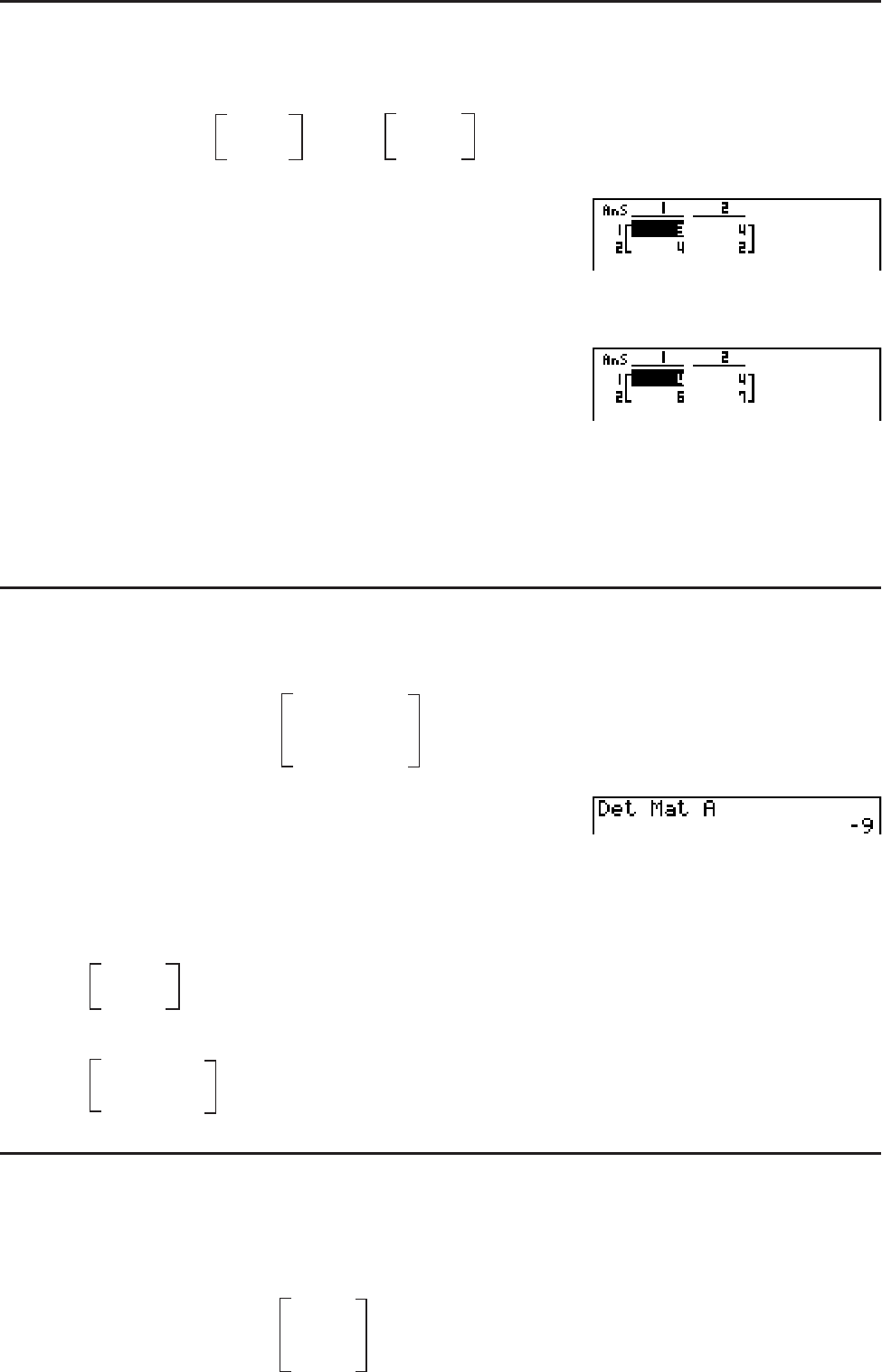
S Determinant [OPTN]-[MAT]-[Det]
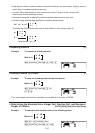
Example Obtain the determinant for the following matrix:
Matrix A =
1 2 3
4 5 6
−1 −2 0
*(MAT)(Det)(Mat)
?T(A)U
• Determinants can be obtained only for square matrices (same number of rows and columns).
Trying to obtain a determinant for a matrix that is not square produces an error.
• The determinant of a 2 s 2 matrix is calculated as shown below.
|A|=
a
11
a
12
=a
11
a
22
–a
12
a
21
a
21
a
22
• The determinant of a 3 s 3 matrix is calculated as shown below.
=a
11
a
22
a
33
+ a
12
a
23
a
31
+ a
13
a
21
a
32
–a
11
a
23
a
32
– a
12
a
21
a
33
– a
13
a
22
a
31
a
11
a
12
a
13
a
21
a
22
a
23
a
31
a
32
a
33
|A|=
S Matrix Transposition [OPTN]-[MAT]-[Trn]
A matrix is transposed when its rows become columns and its columns become rows.
Example To transpose the following matrix:
Matrix A =
12
34
56
A=
1
1
2 1
2 3
2 1
B=
A=
1
1
2 1
2 3
2 1
B=