5-23
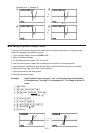
2. Specify the recursion type.
(TYPE)(
a
n
) ... {general term of sequence a
n
}
(
a
n
+1
) ... {linear two-term recursion}
(
a
n
+2
) ... {linear three-term recursion}
3. Input the recursion formula.
4. Specify the table range. Specify a start point and end point for
n. If necessary, specify a
value for the initial term, and a pointer start point value if you plan to graph the formula.
5. Display the recursion formula number table.
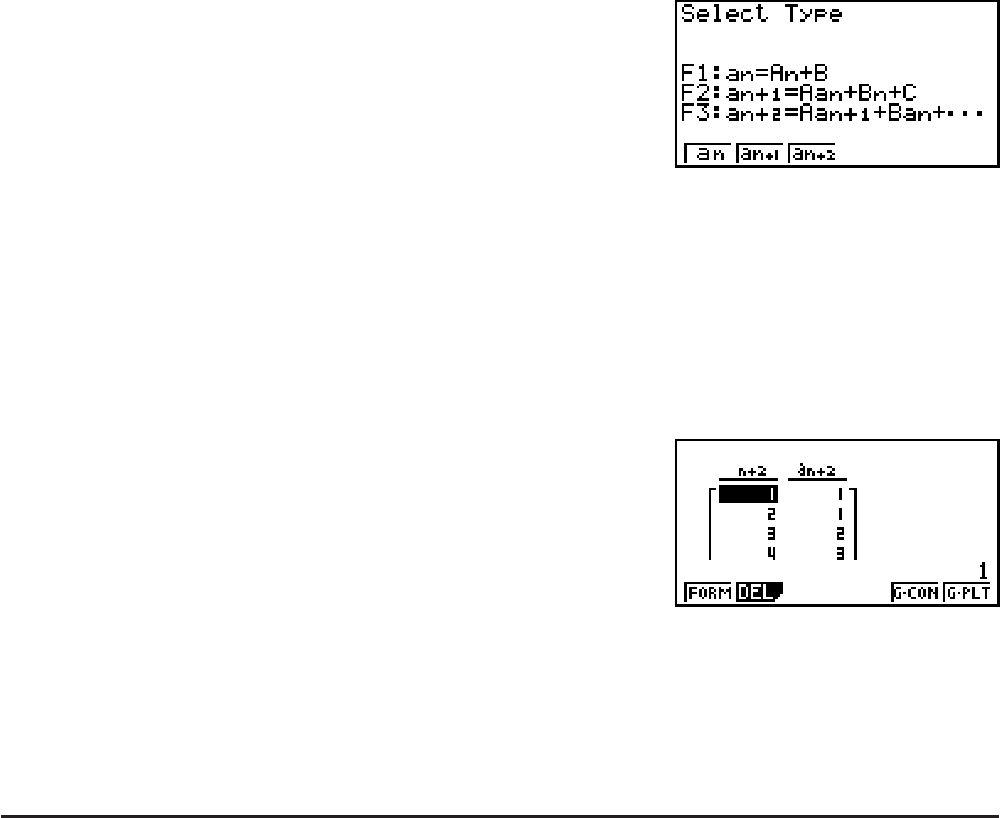
Example Generate a number table from recursion between three terms as
expressed by
a
n
+2
= a
n
+1
+ a
n
, with initial terms of a
1
= 1, a
2
= 1 (Fibonacci
sequence), as n changes in value from 1 to 6.
K RECUR
(TYPE)(
a
n
+2
)
(n.a
n
··)(a
n
+1
)(a
n
)U
(SET)(a
1
)@UEU@U@U)
(TABL)
* The first two values correspond
to a
1
= 1 and a
2
= 1.
• Pressing (FORM) will return to the screen for storing recursion formulas.
• Specifying “On” for the “3Display” of the Setup screen causes the sum of each term to be
included in the table.
I Graphing a Recursion Formula
After generating a number table from a recursion formula, you can graph the values on a line
graph or plot type graph.
1. From the Main Menu, enter the RECUR mode.
2. Make V-Window settings.
3. Specify the recursion formula type and input the formula.
4. Specify the table range, and start and ending values for
n. If necessary, specify the initial
term value and pointer start point.
5. Select the line style for the graph.
6. Display the recursion formula number table.
7. Specify the graph type and draw the graph.
(G
• CON) ... line graph
(G
• PLT) ... plot type graph
Example Generate a number table from recursion between two terms as
expressed by
a
n
+1
= 2a
n
+ 1, with an initial term of a
1
= 1, as n changes in
value from 1 to 6. Use the table values to draw a line graph.
Use the following V-Window settings.
Xmin = 0, Xmax = 6, Xscale = 1
Ymin = –15, Ymax = 65, Yscale = 5