8-12
I Jump Commands (JUMP)
Dsz
Function: This command is a count jump that decrements the value of a control variable by 1,
and then jumps if the current value of the variable is zero.
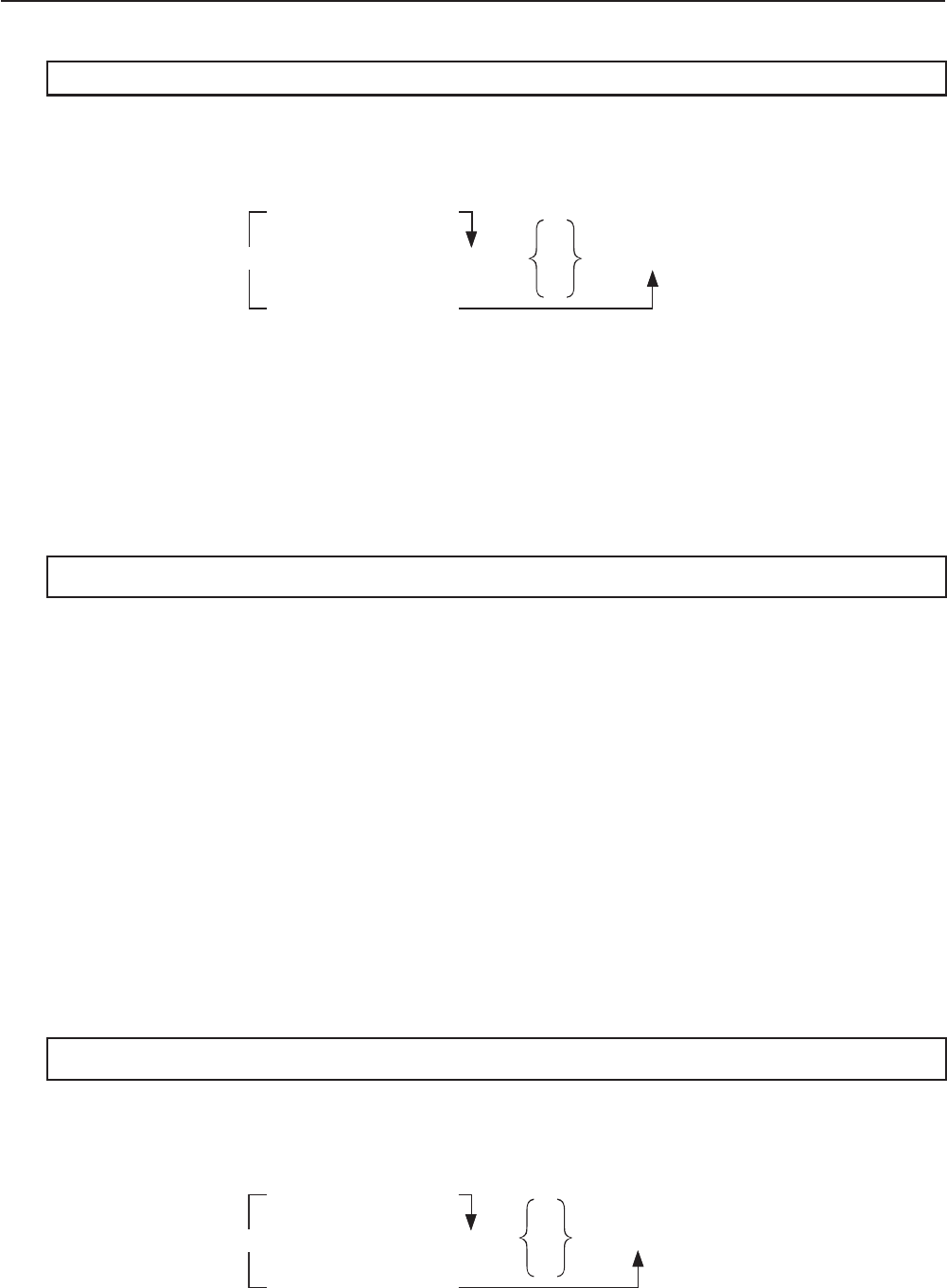
Syntax:
Variable Value x 0
Dsz <variable name> : <statement>
_
:
^
<statement>
Variable Value = 0
Parameters: variable name: A to Z,
r,
Q
[Example] Dsz B : Decrements the value assigned to variable B by 1.
Description: This command decrements the value of a control variable by 1, and then tests
(checks) it. If the current value is non-zero, execution continues with the next statement. If the
current value is zero, execution jumps to the statement following the multi-statement command
(:), display command (<), or carriage return (=).
Goto~Lbl
Function: This command performs an unconditional jump to a specified location.
Syntax: Goto <label name> ~ Lbl <label name>
Parameters: label name: value (0 to 9), variable (A to Z,
r,
Q
)
Description:
• This command consists of two parts: Goto
n (where n is a parameter as described above)
and Lbl n (where n is the parameter referenced by Goto n). This command causes program
execution to jump to the Lbl-statement whose n parameter matches that specified by the
Goto-statement.
• This command can be used to loop back to the beginning of a program or to jump to any
location within the program.
• This command can be used in combination with conditional jumps and count jumps.
• If there is no Lbl-statement whose value matches that specified by the Goto-statement, an
error occurs.
Isz
Function: This command is a count jump that increments the value of a control variable by 1,
and then jumps if the current value of the variable is zero.
Syntax:
Variable Value x 0
Isz <variable name> : <statement>
_
:
^
<statement>
Variable Value = 0
Parameters: variable name: A to Z,
r,
Q
[Example] Isz A : Increments the value assigned to variable A by 1.


















