288 Configuring Switch Information
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Defining Rapid Spanning Tree
While the classic spanning tree prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops on a general network topology,
convergence can take 30-60 seconds. The delay allows time to detect possible loops, and propagate
status changes.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) detects and uses network topologies that allow a faster
convergence of the spanning tree, without creating forwarding loops. To open the Rapid Spanning
Tree (RSTP) settings page, click
Switch
→
Spanning Tree
→
Rapid Spanning Tree
in the tree view.
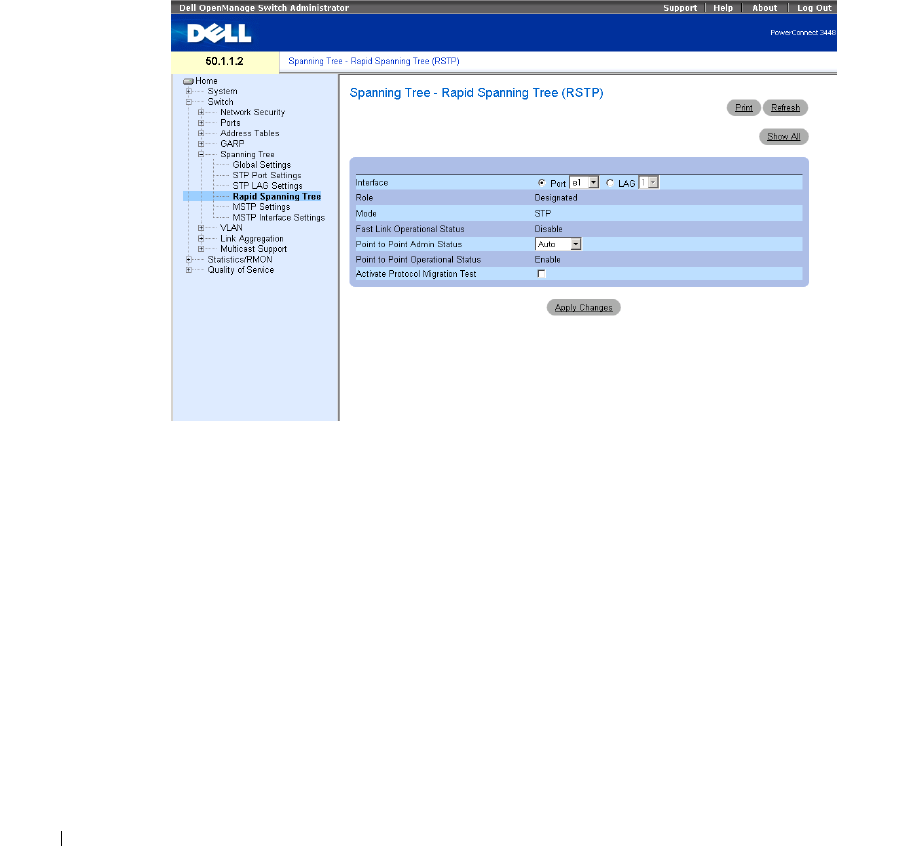
Figure 7-25. Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) settings
The Spanning Tree RSTP page contains the following fields:
Interface
— Port or LAG for which you can view and edit RSTP settings.
State
— Disables RSTP state of the selected interface.
Role
—Indicates the port role assigned by the STP algorithm in order to provide STP paths. The
possible field values are:
Root—Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to root switch.
Designated
—Indicates that the port or LAG via which the designated switch is attached to the LAN.
Alternate
—Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
Backup
—Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree
leaves. Backup ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a point-to-point link.
Backup ports also occur when a LAN has two or more connections connected to a shared segment.
Disabled
—Indicates the port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.


















