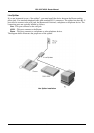
DSL-524T ADSL Router Manual
100
Networks attached to the Internet are assigned class types that determine the maximum number of
possible hosts per network. The previous figure illustrates how the net and host portions of the IP
address differ among the three classes. Class A is assigned to networks that have more than 65,535
hosts; Class B is for networks that have 256 to 65534 hosts; Class C is for networks with less than 256
hosts.
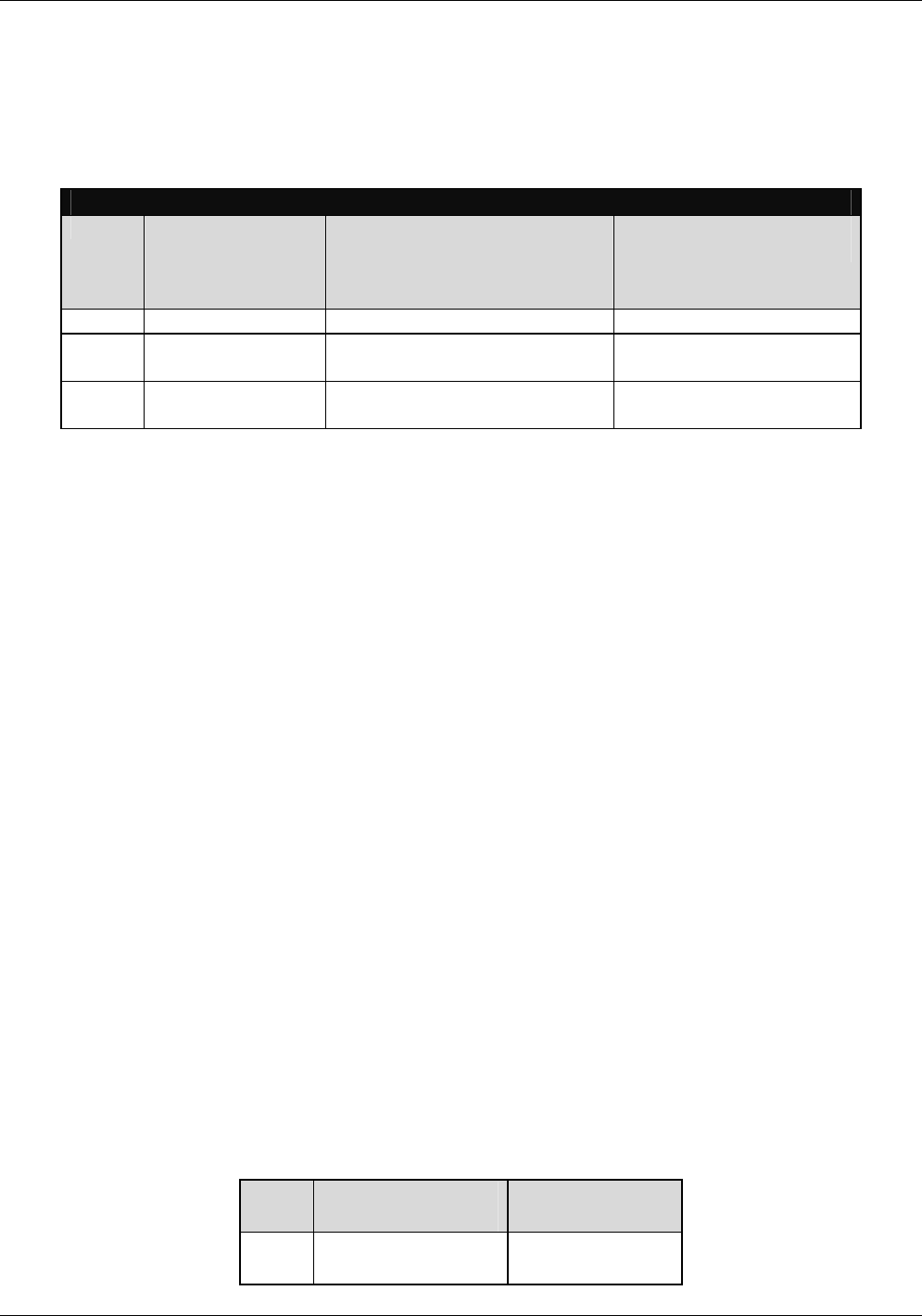
IP Network Classes
Class Maximum
Number of
Networks in
Class
Network Addresses
(Host Portion in
Parenthesis)
Maximum Number of
Hosts per Network
A 126 1(.0.0.0) to 126(.0.0.0) 16,777,214
B 16,382 128.1(.0.0) to 191.254(
.0.0)
65,534
C 2,097,150 192.0.1(.0) to 223.255.254
(.0)
254
Note: All network addresses outside of these ranges (Class D and E) are either reserved or
set aside for experimental networks or multicasting.
When an IP address's host portion contains only zero(s), the address identifies a network and not a host.
No physical device may be given such an address.
The network portion must start with a value from 1 to 126 or from 128 to 223. Any other value(s) in
the network portion may be from 0 to 255, except that in class B the network addresses 128.0.0.0 and
191.255.0.0 are reserved, and in class C the network addresses 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.0 are
reserved.
The value(s) in the host portion of a physical device's IP address can be in the range of 0 through 255
as long as this portion is not all-0 or all-255. Values outside the range of 0 to 255 can never appear in
an IP address (0 to 255 is the full range of integer values that can be expressed with eight bits).
The network portion must be the same for all the IP devices on a discrete physical network (a single
Ethernet LAN, for example, or a WAN link). The host portion must be different for each IP device —
or, to be more precise, each IP-capable port or interface — connected directly to that network.
The network portion of an IP address will be referred to in this manual as a network number; the host
portion will be referred to as a host number.
To connect to the Internet or to any private IP network that uses an Internet-assigned network number,
you must obtain a registered IP network number from an Internet-authorized network information
center. In many countries you must apply through a government agency, however they can usually be
obtained from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
If your organization's networks are, and will always remain, a closed system with no connection to the
Internet or to any other IP network, you can choose your own network numbers as long as they
conform to the above rules.
If your networks are isolated from the Internet, e.g. only between your two branch offices, you can
assign any IP Addresses to hosts without problems. However, the Internet Assigned Numbers
Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP Addresses specifically for private
(stub) networks:
Clas
s
Beginning
Address
Ending
Address
A 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.25
5