Pressure Systems, Inc. 98RK-1 & 9816 User’s Manual©
Page 25 www.PressureSystems.com
2.3.4.5 LEAK Mode Inputs
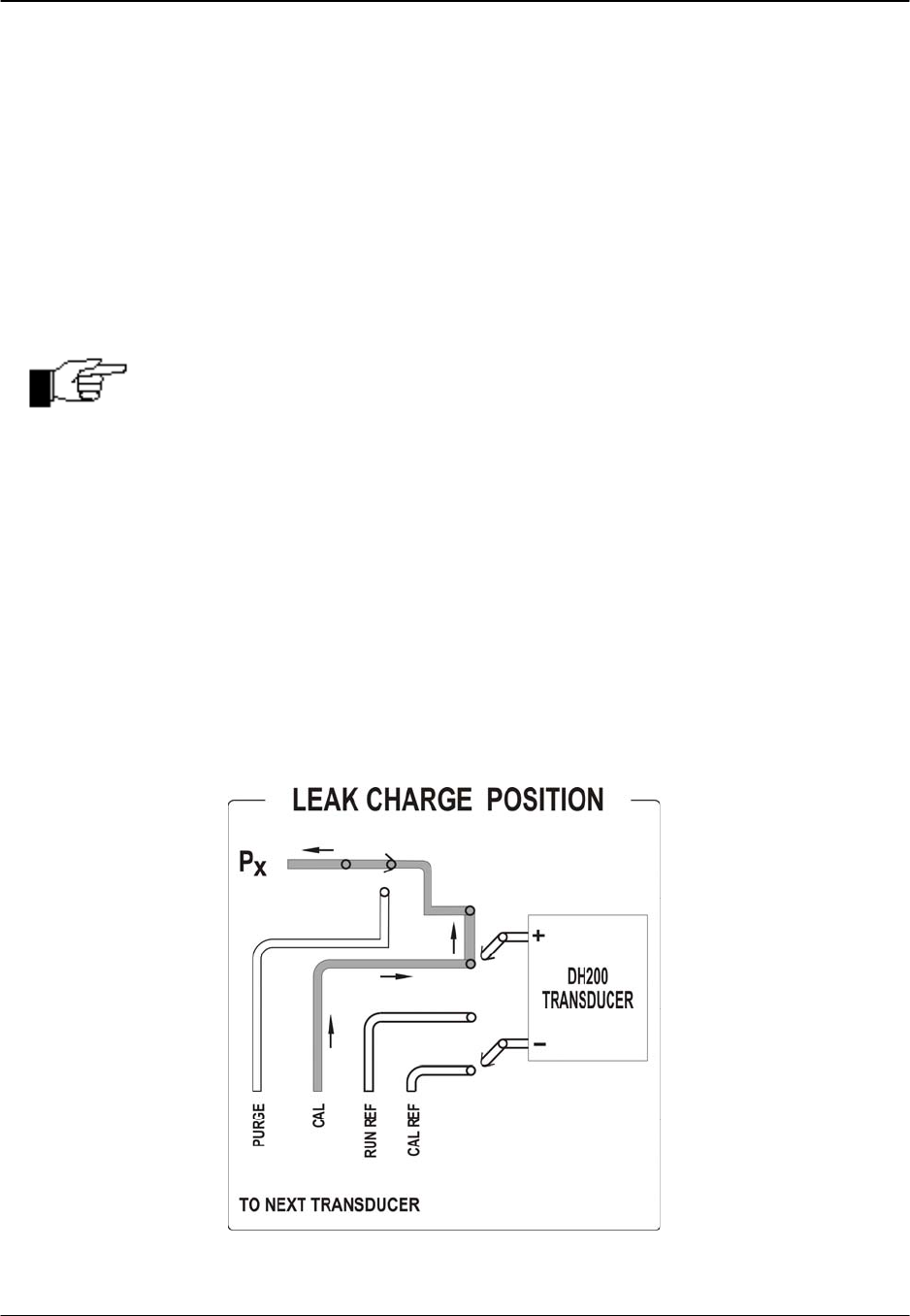
The purge/leak-charge valve design includes a leak check feature capable of testing the
integrity of user pneumatic connections as well as those within the 9816 module. For the leak
mode to be used, all RUN mode pressure inputs must be dead-ended (closed) by the user.
(Contact the PSI Sales Department for availability of an external leak check valve) When the
9816 is commanded into the LEAK/CHARGE position, the CAL 1-8 input ports will be
pneumatically connected to the module run side inputs. Common reference modules will
connect only the numbered run side inputs to CAL (RUN REF is not charged). True differential
(reference per port) modules will connect both the measurement input and reference port to
CAL. While in the LEAK position, a test pressure may be applied thought the CAL port which
will charge the dead-ended run side tubulation.
Note
Test pressures applied to the CAL port during leak check operation
must not exceed the full scale pressure of any internal transducer.
Once the lines are charged, the 9816 may be commanded back to the RUN position. This will
reattach the charged run side lines to their corresponding internal transducer. Consecutive
pressure readings from the 9816 will now allow user to determine the line leak rates. (Factory
testing allows a maximum leak rate of 2% in two (2) minutes.) Once returned to the RUN
position, lack of pressure indicates a gross leak. A slowly declining pressure indicates a slight
leak. A leak is more difficult to detect as tubing volume increases. In the case of true differential
units where both sides of the sensor are pressurized with the leak test pressure, an initial
differential pressure of 0.0 psi should be measured when the unit is placed in the RUN position.
If the measurement or RUN side of the channel leaks at a rate greater than the reference side, a
resulting negative differential pressure will be measured. Likewise, if the reference port tubing
leaks at a rate greater than the measurement side, a resulting positive differential pressure will
be measured.
Figure 2.7