Quick Check® SV Series User’s Guide A - 5
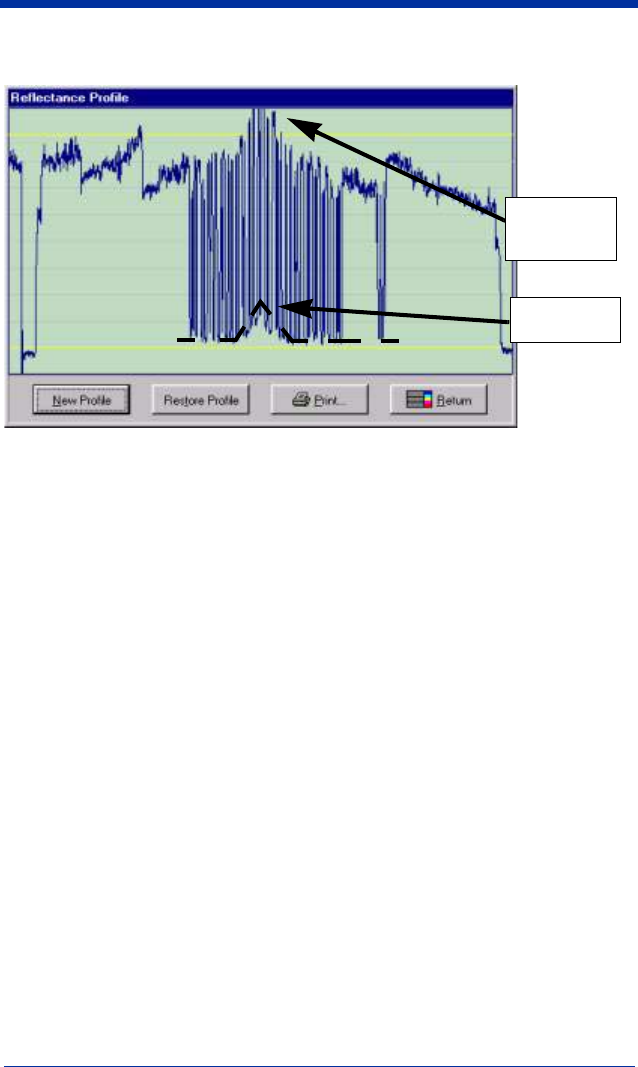
Figure 3 - Examples of Scan Profile Parameters Out of Range
Calibration Hints
Calibration is used to normalize reflectance calculations to known (and/or
traceable) values in absolute units of % reflectance. Calibration affects
reflectance calculations only. Calibration does not affect any other calculations
or ability to decode a symbol, etc. The scanner gain and offset settings have the
major effect on scanning performance. Keeping the scanner signal linear
(between the yellow lines as described previously) is very helpful for good
decoding, but is CRUCIAL for reflectance measurements. The calibration
procedure will not be successful unless the bar code signal is proper.
There may be cases in applications where the material being analyzed requires
a scanner gain and offset setting that will not allow calibration with the standard
SV calibration symbol. In most cases this is due to a low contrast material (such
as brown corrugated) that will make the signal level on the calibration symbol go
past the yellow lines. In cases like this there are two basic choices to make:
1. Do not use parameters that involve absolute units of reflectance as fail-
ure criteria. These parameters include Symbol Contrast, Overall ISO
Grade, PCS, Rmax, and Rmin.
2. If reflectance parameters are required to be analyzed in the application,
a calibration symbol can be created from the material being analyzed.
Contact Hand Held Products Technical Assistance (see page 9-1) for
details.
All of bar code
signal not
lines
Bottom of bar
code signal
not “flat”
between yellow


















