Advanced Configuration and Management Guide
16 - 10
Static Ports
Static ports are permanent members of the protocol VLAN. he ports remain active members of the VLAN
regardless of whether the ports receive traffic for the VLAN’s protocol. You must explicitly identify the port as a
static port when you add it to the VLAN. Otherwise, the port is dynamic and is subject to aging out.
In addition, static ports never “leak” broadcast packets of other protocol types. (See “Broadcast Leaks” on page
16-10.)
Excluded Ports
If you want to prevent a port in a port-based VLAN from ever becoming a member of a protocol, IP sub-net, IPX
network, or AppleTalk cable VLAN configured in the port-based VLAN, you can explicitly exclude the port. ou
exclude the port when you configure the protocol, IP sub-net, IPX network, or AppleTalk cable VLAN.
Broadcast Leaks
Dynamic ports differ from static ports in an important way. Static ports never allow broadcasts for protocols other
than the protocol of the VLAN to be forwarded on the port. Thus, an IP protocol VLAN forwards only IP broadcast
packets and never broadcasts any Layer 3 broadcasts of other protocol types. f you want to ensure that no
broadcasts other than those of the VLAN’s protocol get through, use static ports.
Dynamic ports “leak” every eighth broadcast packet of another protocol type through the port. Thus, if an IP
protocol VLAN receives eight AppleTalk broadcast packets, the VLAN port drops the first seven packets but sends
the eighth packet. his behavior enables a PC, Macintosh computer, or workstation that joins the network to find
its servers, even if the LAN segment the device is on is configured as part of a protocol VLAN for a different
protocol. For example, if a few of your network users have Macintosh computers, they can still find their printers or
other servers even if the network segment they are on is part of an IP protocol VLAN.
The VLAN ports maintain separate counters for each protocol. Thus, if a port in an IP protocol VLAN receives four
AppleTalk broadcast packets and four DECnet broadcast packets, the port still does not forward any of the
packets. ly when the port receives eight AppleTalk broadcast packets or eight DECnet broadcast packets does
the port send the eighth packet of that protocol type.
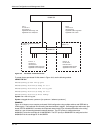
Figure 16.8 shows an example of a Layer 3 IP protocol VLAN with dynamic ports. Since the ports have dynamic
membership, they are “leaky”. They forward every eighth broadcast packet of non-IP protocols. For example,
when the Macintosh computer sends its eighth broadcast packet, the VLAN forwards the packet. In a VLAN with
static ports, the VLAN never forwards broadcast packets of other protocol types.
Figure 16.8 Protocol VLAN with “leaky” (dynamic) ports
User-configured port-basedVLAN
Active Dynamic Ports
A CA CAA
Candidate Ports
T
Y
I
T
On
A C