Using operating system controls
Some operating systems offer a way to manage integrated wireless devices and the wireless connection.
For example, Windows provides the Network and Sharing Center that allows you to set up a connection
or network, connect to a network, manage wireless networks, and diagnose and repair network
problems.
To access the Network and Sharing Center, select Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet >
Network and Sharing Center.
For more information, select Start > Help and Support.
Using a WLAN
With a WLAN device, you can access a wireless local area network (WLAN), which is composed of other
computers and accessories that are linked by a wireless router or a wireless access point.
NOTE: The terms wireless router and wireless access point are often used interchangeably.
●
A large-scale WLAN, such as a corporate or public WLAN, typically uses wireless access points
that accommodate a large number of computers and accessories and can separate critical network
functions.
●
A home or small office WLAN uses a wireless router, which allows several wireless and wired
computers to share an Internet connection, a printer, and files without requiring additional pieces
of hardware or software.
To use the WLAN device in the computer, connect to a WLAN infrastructure (provided through a service
provider or a public or corporate network).
Setting up a WLAN
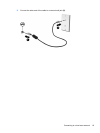
To set up a WLAN and connect to the Internet, you need:
●
A broadband modem (either DSL or cable) (1) and high-speed Internet service purchased from an
Internet service provider (ISP)
●
A wireless router (purchased separately) (2)
●
The wireless computer (3)
The illustration below shows an example of a wireless network installation that is connected to the
Internet.
As your network grows, additional wireless and wired computers can be connected to the network to
access the Internet.
For help in setting up your WLAN, see the information provided by your router manufacturer or your
ISP.
Using a WLAN 15