User Manual - Configuration Guide (Volume 3)
Versatile Routing Platform
Chapter 1
VoIP Configuration
1-2
1.1.1 VoIP Principle
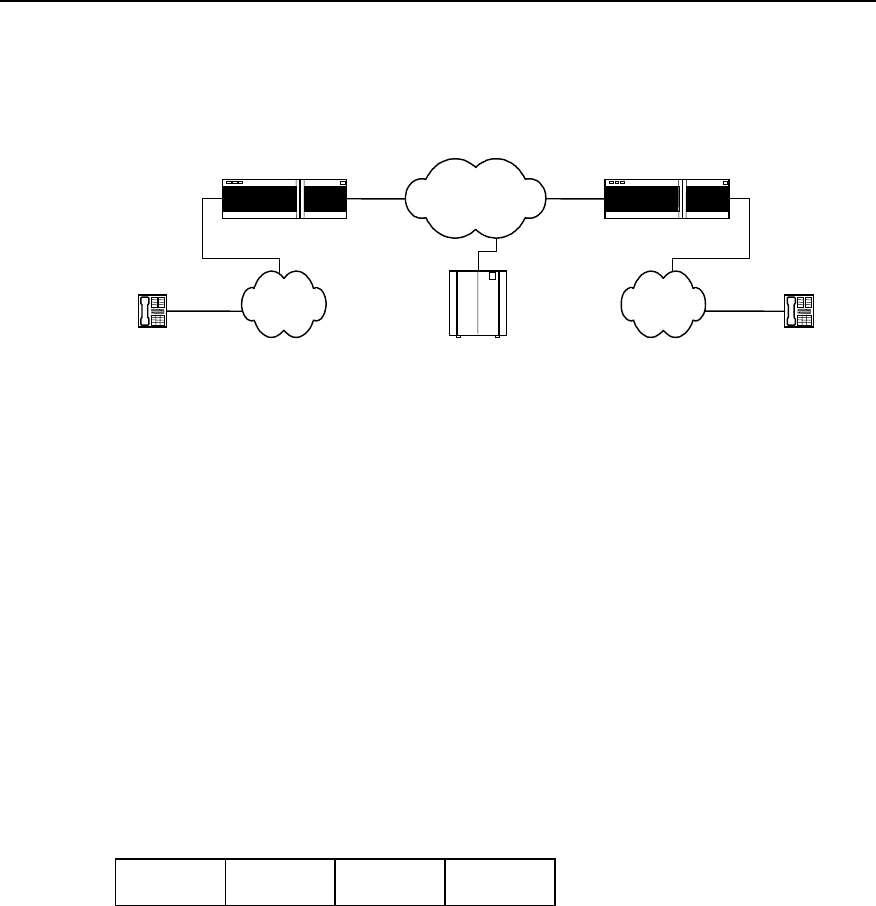
I. Basic composition
Telephone Telephone
IP network
IP voice gateway IP voice gateway
PSTN PSTN
GateKeeper
Figure VC-1-1 Basic composition of the VoIP system
For the plain voice service, all the functions from the caller to the called are
implemented by PSTN, but IP voice service is quite different.
In the above figure, the IP voice gateway provides the port between the IP network and
the public telephone networks (PSTN/ISDN), and user is connected to the IP voice
gateway through the PSTN local loop. The IP voice gateway is responsible for
converting the analogue signals to digital signals, compressing and packetizing so that
they become packet voice signals that can be transmitted over the IP network. Then,
they are sent to the user gateway and the IP voice gateway at the called end reverts the
packets to recognizable analogue voice signals. Once these signals arrive at the called
terminal through PSTN, a communication process from telephone to telephone
completes. In real VoIP networking, you may need gatekeeper to accomplish functions
such as routing and access control.
VoIP uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) in the Transport Layer. Since the UDP
provides connectionless and unreliable datagram service, it is not very appropriate for
real-time application. The current approach is to run the RTP (Real-time Transport
Protocol) over the UDP to enhance function of real-time application.
IP header UDP header
RTP header
Voice load
Figure VC-1-2 VoIP packet format
II. H.323 protocol stack
To realize the VoIP, currently almost all the manufacturers adopt the ITU-T standard
protocol family H.323. The H.323 protocol is implemented in the Application Layer,
which mainly describes the terminals, device and services for multimedia
communication in local area network without quality of service (QoS) guarantee,
including H.225.0, H.245, G.729, G.723.1, G.711, H.261, H.263 and T.120 series, etc.
G.723.1, G.729 and G.711 are audio codec protocols, H.263 and H.261 are video
codec protocols, H.225.0 and H.245 are system control protocols, and the T.120 series
are multimedia data transport protocol.
RTP and its controlled protocols RTCP (RTP Control Protocol) together ensure the
real-timeliness of voice message transmission. The function of RTP is enhanced via
RTCP. RTCP is used to give feedback for the quality of data dispatch. With this


















