User Manual - Configuration Guide (Volume 3)
Versatile Routing Platform
Chapter 3
E1 Voice Configuration
3-1
Chapter 3 E1 Voice Configuration
3.1 Overview of E1 Voice Configuration
3.1.1 Function of E1 Voice
E1 voice refers to the implementation of VoIP function over E1 line, so as to provide
voice transmission mode compatible with data transmission. In order to implement this
function, the corresponding E1 voice port needs to be provided on the router and also a
range of functions suitable for voice transmission over E1 line should be provided. The
networking that adopts E1 line for voice transmission is the same as the ordinary VoIP
networking applications, except that the connection between PSTN switch and the
router is through E1 trunk, and the signaling adopted for the line is R2 signaling (similar
to China No. 1 Signaling) or DSS1 subscriber signaling on ISDN PRI interface. The
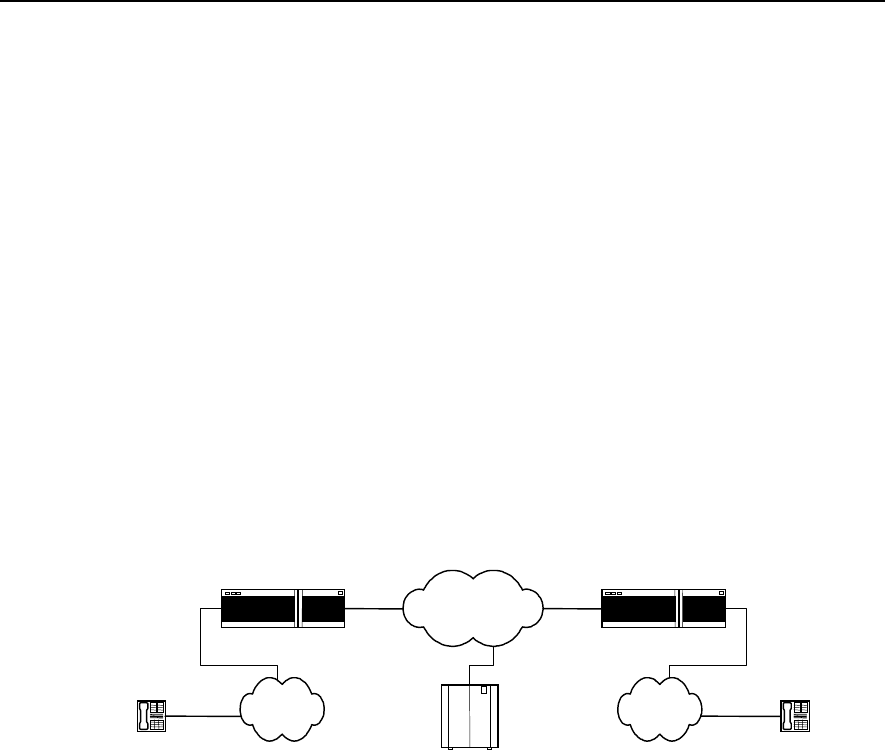
basic networking is shown in the diagram below:
Telephone Telephone
IP network
IP voice gateway
IP voice gateway
PSTN PSTN
Gate Keeper
E1 E1
Figure VC-3-1 Basic Structure of E1 Voice System
Adopting E1 voice mode, the router can provide more channels for voice
communication and supports integrated transmission of data and voice, greatly
enhancing the utilization rate of the router and the range of the services supported.
3.1.2 Usage of cE1/PRI Interface
The physical port of E1 voice is cE1/PRI interface, which is divided into 32 TSs (time
slots) numbered from 0 to 31. The following lists three methods to use this interface:
I. Interface not divided into TSs logically
When used as E1 interface, do not divide it into TSs logically and use the full capability
of the interface for data transmission. The bandwidth of the interface is 2Mbit/s (TSs 0
to 31) and its logical attribute is equal to the synchronous serial port with rate of 2Mbit/s.
On the interface, link layer protocols such as PPP, FR, LAPB, X.25 and HDLC, and
network protocols such as IP and IPX, are supported.


















