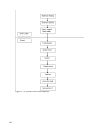
14. The boot loader sets the IDT with null interrupt handlers. It puts the system parameters obtained
from the BIOS and the parameters passed to the operating system into the first page frame.
15. The boot loader identifies the model of the processor. It loads the gdtr and idtr registers with the
addresses of the Global Descriptor Table and Interrupt Descriptor Table, and jumps to the
start_kernel() function.
16. start_kernel() completes the kernel initialization by initializing Page Tables, Memory
Handling Data Structures, IDT tables, the slab allocator (described in Section 5.5.3.6), system date,
and system time.
17. The boot loader uncompress the initial RAM file system initrd, mounts it, and then executes
/linuxrc.
18. The boot loader unmounts initrd, mounts the root file system, and executes /sbin/init. It
resets the pid table to assign process ID one to the init process.
19. /sbin/init determines the default run level from /etc/inittab and performs the following
basic system initialization by executing the script /etc/init.d/boot.
1. Allows an administrator to perform interactive debugging of the startup process by executing the
/etc/sysconfig/boot script.
2. Mounts the /proc special file system.
3. Mounts the /dev/pts special file system.
4. Executes /etc/init.d/boot.local, which was set by an administrator to perform site-
specific setup functions.
5. If file /var/lib/YaST2/runme_at_boot exists, finishes YaST2 installation from previous session.
6. If file /var/lib/YaST2/run_suseconfig exists, executes /sbin/SuSEconfig to configure the operating
system.
7. Performs run-level specific initialization by executing startup scripts defined in
/etc/inittab. The scripts are named /etc/init.d/rcX.d, where X is the default run
level. The default run level for a SLES system in the evaluated configuration is 3. The
following lists some of the initializations performed at run level 3.
• Saves and restores the system entropy tool for higher quality random number generation.
• Configures network interfaces.
• Starts the system logging daemons.
• Starts the sshd daemon.
• Starts the atd daemon
• Starts the cron daemon.
• Probes hardware for setup and configuration.
• Starts the program agetty.
For more detail about services started at run level 3, refer to the scripts in
/etc/init.d/rc3.d on a SLES system.
For detailed information about the boot process, see http://tldp.org/HOWTO/Linux-Init-HOWTO.html#toc1.
Figure 5-79 schematically describes the boot process of System x servers.
159