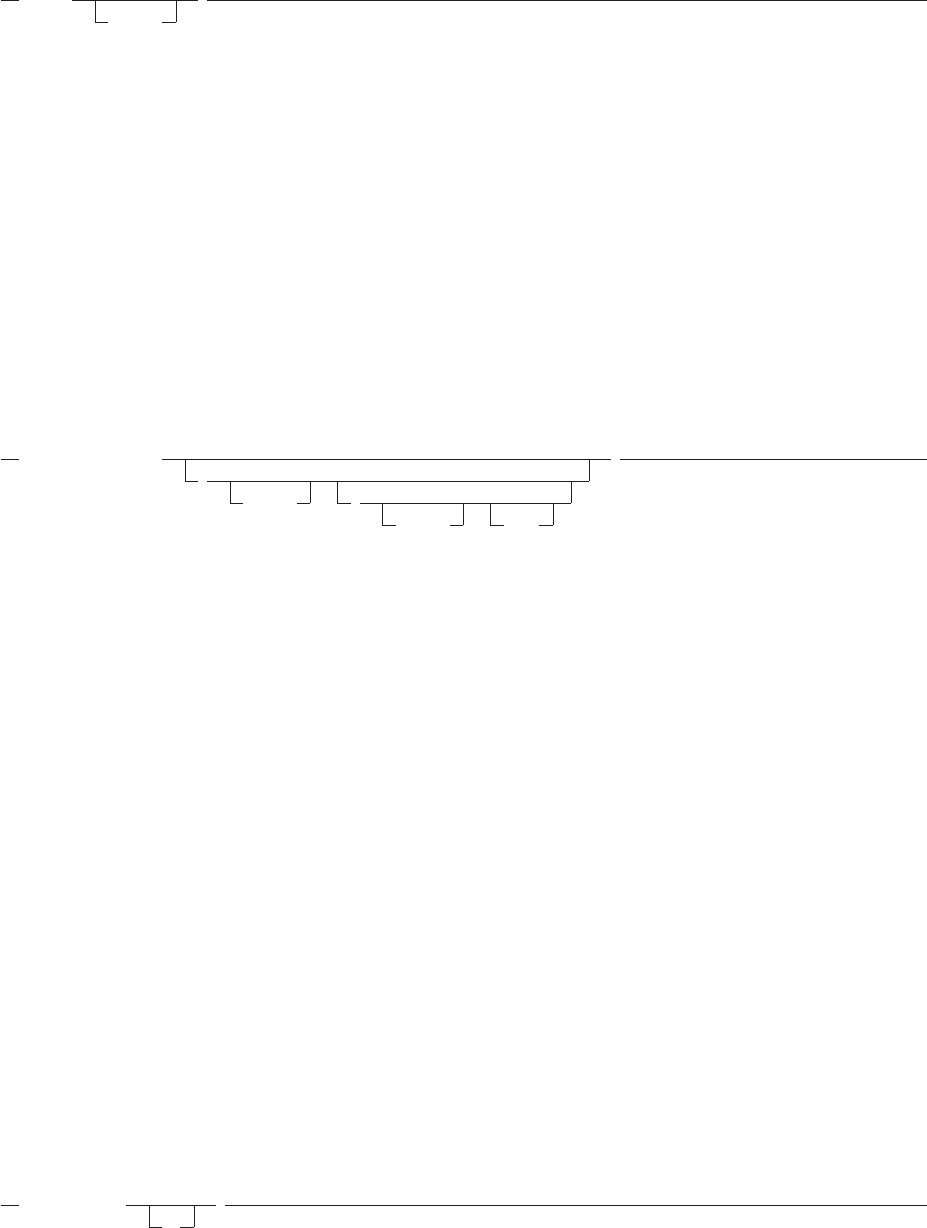
TRACE
TRACE(
option
)
returns trace actions currently in effect and, optionally, alters the setting.
If you specify option, it selects the trace setting. It must be one of the valid prefixes ? or ! or one of the
alphabetic character options associated with the TRACE instruction (that is, starting with A, C, E, F, I, L, N,
O, R,orS) or both.
Unlike the TRACE instruction, the TRACE function alters the trace action even if interactive debug is
active. Also unlike the TRACE instruction, option cannot be a number.
Here are some examples:
TRACE() -> '?R' /* maybe */
TRACE('O') -> '?R' /* also sets tracing off */
TRACE('?I') -> 'O' /* now in interactive debug */
TRANSLATE
TRANSLATE(string
,
tableo ,
tablei ,pad
)
returns string with each character translated to another character or unchanged. You can also use this
function to reorder the characters in string.
The output table is tableo and the input translation table is tablei. TRANSLATE searches tablei for each
character in string. If the character is found, then the corresponding character in tableo is used in the
result string; if there are duplicates in tablei, the first (leftmost) occurrence is used. If the character is not
found, the original character in string is used. The result string is always the same length as string.
The tables can be of any length. If you specify neither translation table and omit pad, string is simply
translated to uppercase (that is, lowercase a–z to uppercase A–Z), but, if you include pad, the language
processor translates the entire string to pad characters. tablei defaults to XRANGE('00'x,'FF'x), and tableo
defaults to the null string and is padded with pad or truncated as necessary. The default pad is a blank.
Here are some examples:
TRANSLATE('abcdef') -> 'ABCDEF'
TRANSLATE('abbc','&','b') -> 'a&&c'
TRANSLATE('abcdef','12','ec') -> 'ab2d1f'
TRANSLATE('abcdef','12','abcd','.') -> '12..ef'
TRANSLATE('APQRV',,'PR') -> 'AQV'
TRANSLATE('APQRV',XRANGE('00'X,'Q')) -> 'APQ '
TRANSLATE('4123','abcd','1234') -> 'dabc'
Note: The last example shows how to use the TRANSLATE function to reorder the characters in a string.
In the example, the last character of any four-character string specified as the second argument
would be moved to the beginning of the string.
TRUNC (Truncate)
TRUNC(number
,n
)
returns the integer part of number and n decimal places. The default n is 0 and returns an integer with no
Functions
Chapter 14. Functions 195


















