MSS User Guide 4: Configuration
4-14
Flow Control
Note: RTS/CTS Flow Control is not available in RS-485 mode.
Both RTS/CTS (hardware) and XON/XOFF (software) flow control methods can be used
on the MSS. RTS/CTS controls data flow by sending serial port signals between two
connected devices. XON/XOFF controls data flow by sending particular characters
through the data stream: Ctrl-Q to accept data (XON) and Ctrl-S when data cannot be
accepted (XOFF).
Note: Applications that use Ctrl-Q and Ctrl-S will conflict with XON/XOFF flow control, in
which case RTS/CTS is recommended.
To switch between flow control methods, use the Change Port Flow Control command
followed by the preferred method. If you do not wish to use flow control at all, specify
None.
Figure 4-48: Enabling Recommended Flow Control for MSS-VIA and MSS4
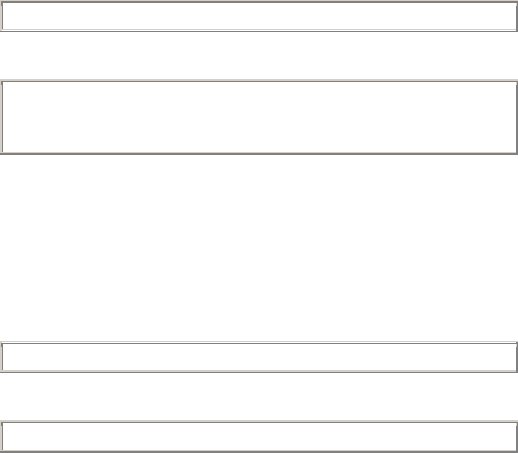
Local>> CHANGE PORT 1 FLOW CONTROL CTSRTS
Figure 4-49: Enabling Recommended Flow Control for MSS100
Local>> CHANGE FLOW CONTROL CTSRTS
or
Local>> CHANGE FLOW CONTROL XON
If you're using XON/XOFF flow control, the XON/XOFF characters will be removed from
the data stream by default. To prevent this removal, the Passflow option can be enabled.
However, passflow is unnecessary in most situations. See the Commands chapter in the
MSS Reference Manual for more information.
Figure 4-50: Enabling Passflow for MSS-VIA and MSS4
Local>> CHANGE PORT 1 PASSFLOW ENABLE
Figure 4-51: Enabling Passflow for MSS100
Local>> CHANGE PASSFLOW ENABLE
Modems and Modem Signaling
The following sections explain some of the MSS options that are typically considered to
be modem-related. They do not apply exclusively to modems, but to communications
devices in general. Most options are mutually exclusive when enabled.
Note: Modem Emulation Mode, in which the MSS acts like a modem and only accepts
AT modem commands, is discussed in 5:Using the MSS.
After configuring modem-related settings, refer to the Modem Configuration Checklist in
5:Using the MSS.


















