171
FINS/TCP Method Section 7-4
7-4 FINS/TCP Method
7-4-1 Overview
FINS/TCP Features
The FINS/TCP method is a FINS communications method that uses the TCP/
IP protocol. TCP/IP is a connection-type communications protocol. Before a
message is sent from one node to another, it is necessary to establish a vir-
tual circuit, i.e., a connection. Once a connection has been established, com-
munications are quite reliable. The arrival of data that is sent via the
connection is confirmed by an acknowledgement (ACK) response, and retries
are executed automatically as required.
The FINS/TCP method has been newly added to the CS1W-ETN21 and
CJ1W-ETN21 Ethernet Units. When FINS/TCP is used, it must be determined
which node is the server and which is the client.
For communications between a personal computer and a PLC, the computer
should normally be set as the client and the PLC as the server. For communi-
cations between two PLCs, either one can be set as the client and the other
as the server.
Compared to the FINS/UDP method, the FINS/TCP method has the following
characteristics.
• Data transmission is more reliable, due to factors such as retry process-
ing at the TCP/IP layer. The FINS/TCP method is thus better suited to
dealing with communications errors in an IP network that spans several
layers.
• Remote clients can be restricted by means of settings at the server (i.e.,
the server can be protected from access by non-specified IP addresses).
• Broadcasting cannot be used.
• TCP/IP has various retry procedures, and this tends to lower its perfor-
mance in comparison with UDP/IP.
• There is a limit to the number of connections that can be made (i.e., 16
connections maximum), and any given node can communicate only with
up to 16 other nodes at a time.
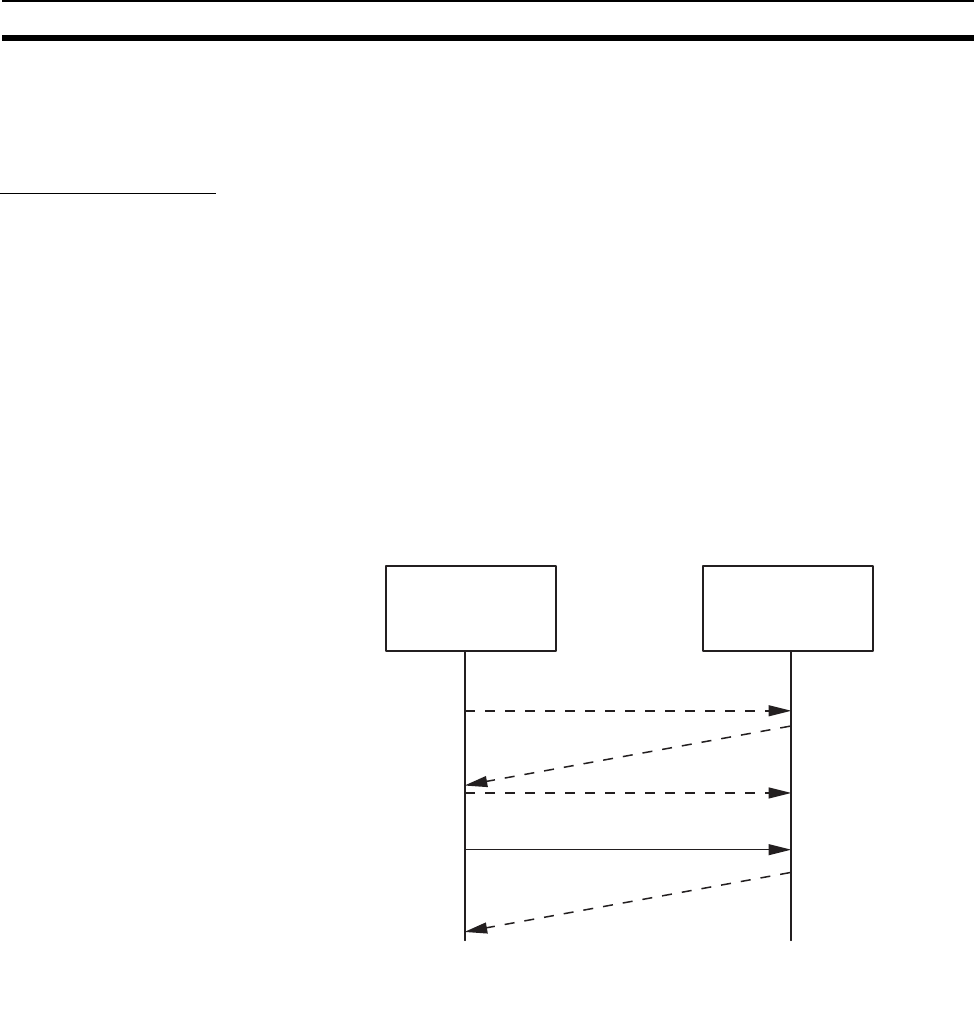
Node
(Client)
Data transmission 1
Request to establish a connection
Node
(Server)
Connection established
Acknowledgement
Acknowledgement
An acknowledgement is received whenever a
connection is established or data is sent, so
transmissions are more reliable but somewhat slower.


















