7-9
Using Passwords, Port Security, and Authorized IP Managers To Protect Against Unauthorized Access
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Using Passwords, Port
Security, and Authorized IP
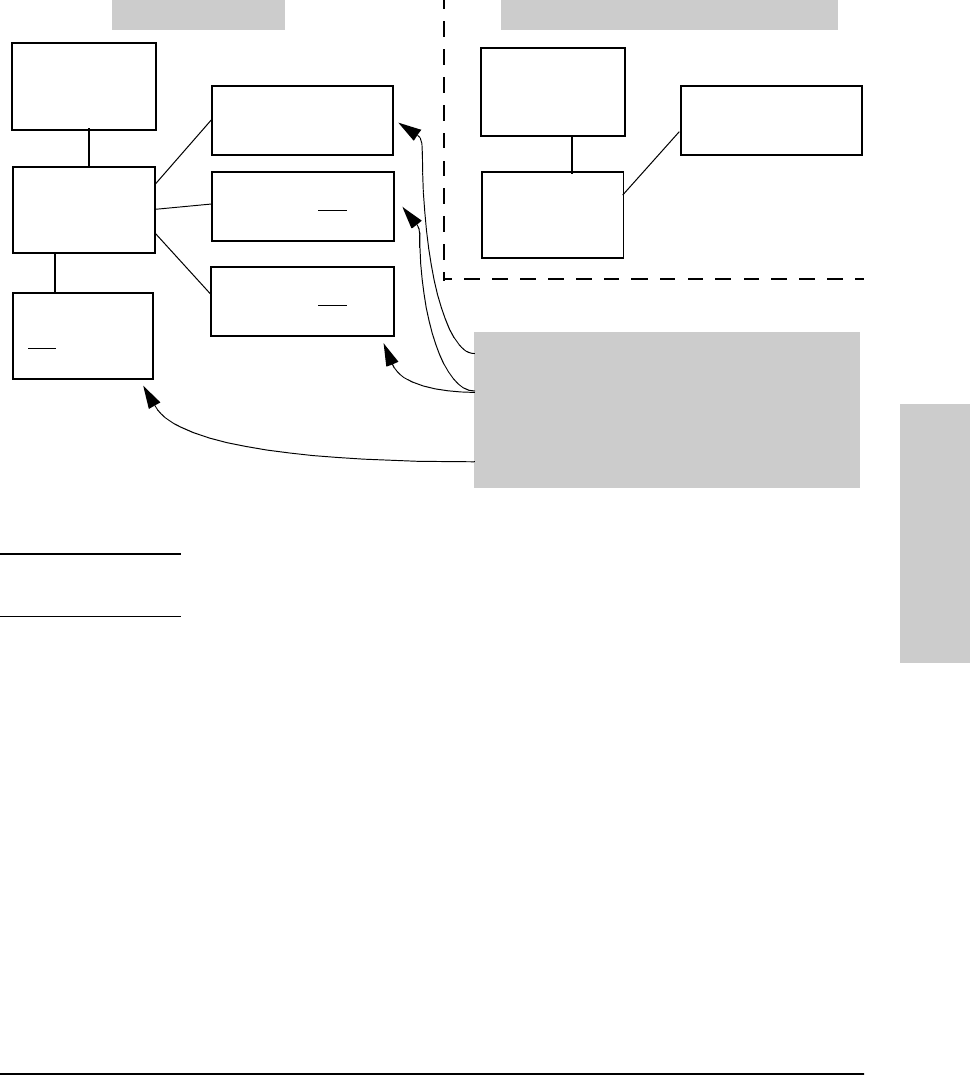
Figure 7-3. Example of How Port Security Controls Access
Note Broadcast and Multicast traffic is not “unauthorized” traffic, and can be read
by intruders connected to a port on which you have configured port security.
Trunk Group Exclusion
Port security does not operate on either a static or dynamic trunk group. If
you configure port security on one or more ports that are later added to a trunk
group, the switch will reset the port security parameters for those ports to the
factory-default configuration. (Ports configured for either Active or Passive
LACP, and which are not members of a trunk, can be configured for port
security.)
Planning Port Security
1. Plan your port security configuration and monitoring according to the
following:
a. On which ports do you want to configure port security?
Switch A
Port Security
Configured
Switch B
MAC Address
Authorized by
Switch A
PC 1
MAC Address
Authorized by Switch A
PC 2
MAC Address NOT
Authorized by Switch A
PC 3
MAC Address NOT
Authorized by Switch A
Switch C
MAC Address
NOT
Authorized
by Switch A
Switch A
Port Security
Configured
Switch B
MAC Address
Authorized by
Switch A
PC 1
MAC Address
Authorized by Switch A
Logical Topology for Access to Switch APhysical Topology
• PC1 can access Switch A.
• PCs 2 and 3 can access Switch B and Switch C, but are
blocked from accessing switch A by the port security
settings in switch A.
• Switch C is not authorized to access Switch A.


















