79
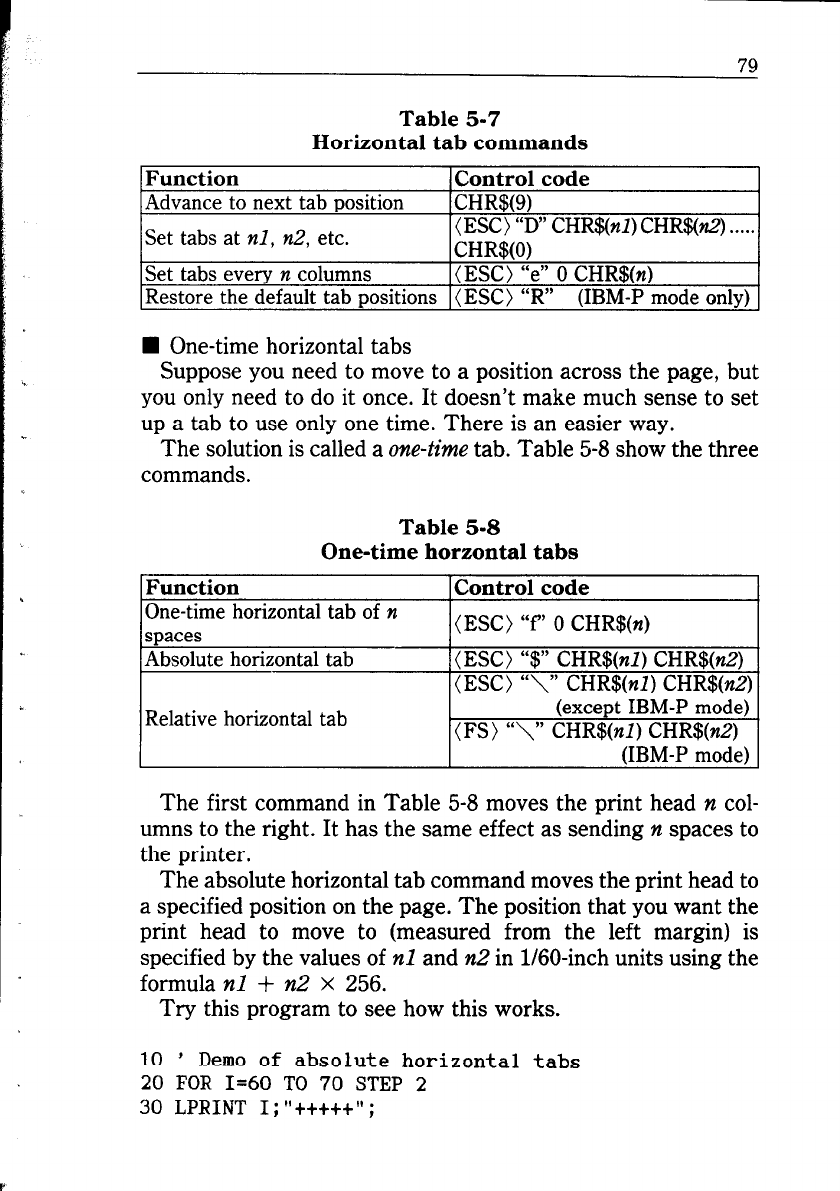
Table 5-7
Horizontal tab commands
Function
Control code
Advance to next tab position
CHR$@)
Set tabs at nl, n2, etc.
(ESC) “D” CHR$(nl) CHR$(n2) . . . . .
CHWO)
Set tabs every n columns
(ESC) “e” 0 CHR$(n)
Restore the default tab positions (ESC) “R”
(IBM-P mode only)
n One-time horizontal tabs
Suppose you need to move to a position across the page, but
you only need to do it once. It doesn’t make much sense to set
up a tab to use only one time. There is an easier way.
The solution is called a one-time tab. Table 5-8 show the three
commands.
Table 5-8
One-time horzontal tabs
Function
One-time horizontal tab of n
spaces
Absolute horizontal tab
Relative horizontal tab
Control code
(ESC) “f” 0 CHR$(n)
(ESC) “$” CHR$(nl) CHR$(nZ)
(ESC) “\” CHR$(nl) CHR$(nZ)
(except IBM-P mode)
(FS) “\” CHR$(nl) CHR$(azZ)
(IBM-P mode)
The first command in Table 5-8 moves the print head n col-
umns to the right. It has the same effect as sending n spaces to
the printer.
The absolute horizontal tab command moves the print head to
a specified position on the page. The position that you want the
print head to move to (measured from the left margin) is
specified by the values of nl and n2 in 1/604nch units using the
formula nl + n2 x 256.
Try this program to see how this works.
10 ’
Demo of absolute horizontal tabs
20 FOR I=60 TO 70 STEP 2
30 LPRINT I ; “ttttt” ;


















