TMP92CM22
2007-02-16
92CM22-139
3. Pulse width measurement
This mode allows measuring the high level width of an external pulse. While
keeping the 16-bit timer/event counter counting (Free running) with the prescaler
output clock input, external pulse is input through the TB1IN0 pin. Then the
capture function is used to load the UC12 values into TB1CP0H/L and
TB1CP1H/L at the rising edge and falling edge of the external trigger pulse
respectively. The interrupt INT4 occurs at the falling edge of TB1IN0.
The pulse width is obtained from the difference between the values of
TB1CP0H/L and TB1CP1H/L and the internal clock cycle.
For example, if the prescaler output clock is 0.8 μs and the difference between
TB1CP0H/L and TB1CP1H/L is 100, the pulse width will be 100 × 0.8 μs = 80 μs.
Additionally, the pulse width that is over the UC12 maximum count time
specified by the clock source can be measured by changing software.
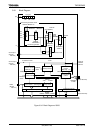
Figure 3.8.15 Pulse Width Measurement
Note: Pulse Width measure by setting “10” to TB1MOD<TB1CPM1:0>. The external interrupt
INT4 is generated in timing of falling edge of TB1IN0 input. In other modes, it is generated
in timing of rising edge of TB1IN0 input.
The width of low level can be measured from the difference between the first C2
and the second C1 at the second INT4 interrupt.
C1 C2
C1
C2 C2
C1
TB1IN0 pin input
(External pulse)
Load into TB0CP0H/L
Count clock
(Prescaler output clock)
Load into TB0CP1H/L
INT4