TMP92CM22
2007-02-16
92CM22-150
(6) The receiving buffers
To prevent overrun errors, the receiving buffers are arranged in a double-buffer
structure.
Received data is stored one bit at a time in receiving buffer 1 (which is a shift
register). When 7 or 8 bits of data have been stored in receiving buffer 1, the stored
data is transferred to receiving buffer 2 (SC0BUF); this causes an INTRX0 interrupt to
be generated.
The CPU only reads receiving buffer 2 (SC0BUF). Even before the CPU reads
receiving buffer 2 (SC0BUF), the received data can be stored in receiving buffer 1.
However, unless receiving buffer 2 (SC0BUF) is read before all bits of the next data
are received by receiving buffer 1, an overrun error occurs. If an overrun error occurs,
the contents of receiving buffer 1 will be lost, although the contents of receiving buffer
2 and SC0CR<RB8> will be preserved.
SC0CR<RB8> is used to store either the parity bit – added in 8-bit UART mode – or
the most significant bit (MSB) – in 9-bit UART mode.
In 9-bit UART mode the wake-up function for the slave controller is enabled by
setting SC0MOD0<WU> to 1; in this mode INTRX0 interrupts occur only when the
value of SC0CR<RB8> is 1.
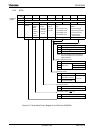
(7) Transmission counter
The transmission counter is a 4-bit binary counter that is used in UART mode and
which, like the receiving counter, counts the SIOCLK clock pulses; a TXDCLK pulse is
generated every 16 SIOCLK clock pulses.
Figure 3.9.4 Generation of Transmission Clock
(8) Transmission controller
• In I/O interface mode
In SCLK output mode with the setting SC0CR<IOC> = 0, the data in the
transmission buffer is output one bit at a time to the TXD0 pin on the rising or
falling edge of the shift clock which is output on the SCLK0 pin, according to the
SC0CR<SCLKS> setting.
In SCLK input mode with the setting SC0CR<IOC> = 1, the data in the
transmission buffer is output one bit at a time on the TXD0 pin on the rising or
falling edge of the SCLK0 input, according to the SC0CR<SCLKS> setting.
• In UART mode
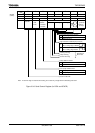
When transmission data sent from the CPU is written to the transmission buffer,
transmission starts on the rising edge of the next TXDCLK, generating a
transmission shift clock TXDSFT.
15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2
SIOCLK
TXDCLK