Where:
Printer_name is the Print Queue name used to store jobs for the corresponding logical
printer.
PS_NAME is the Wireless Print Server name defined in /etc/hosts.
Logical_Printer_name is the logical printer name on the Wireless Print Server. (e.g. L1)
Spooler_directory is the directory you created in Step 6.
Example:
Marketing|RP1_PS123456:\
[T
AB] :lp=:\
[T
AB] :rm=PS_Rm203:\
[T
AB] :rp=L1:\
[T
AB] :sd=/usr/spool/Marketing:\
[T
AB] :mx#0:
Repeat this process for each Logical Printer/Print Queue combination that you wish to create.
LPD on Linux
If using the command line, the procedure is the same as for System V. (above)
On recent Linux distributions, you can use the graphical X-windows interface instead of the
command line. The procedure is described below, but may vary according to your version of
Linux.
1. Start your X-windows shell.
2. Select Control Panel, then Printer Configuration.
3. Select Add. For the printer type, select Remote Unix (lpd) Queue.
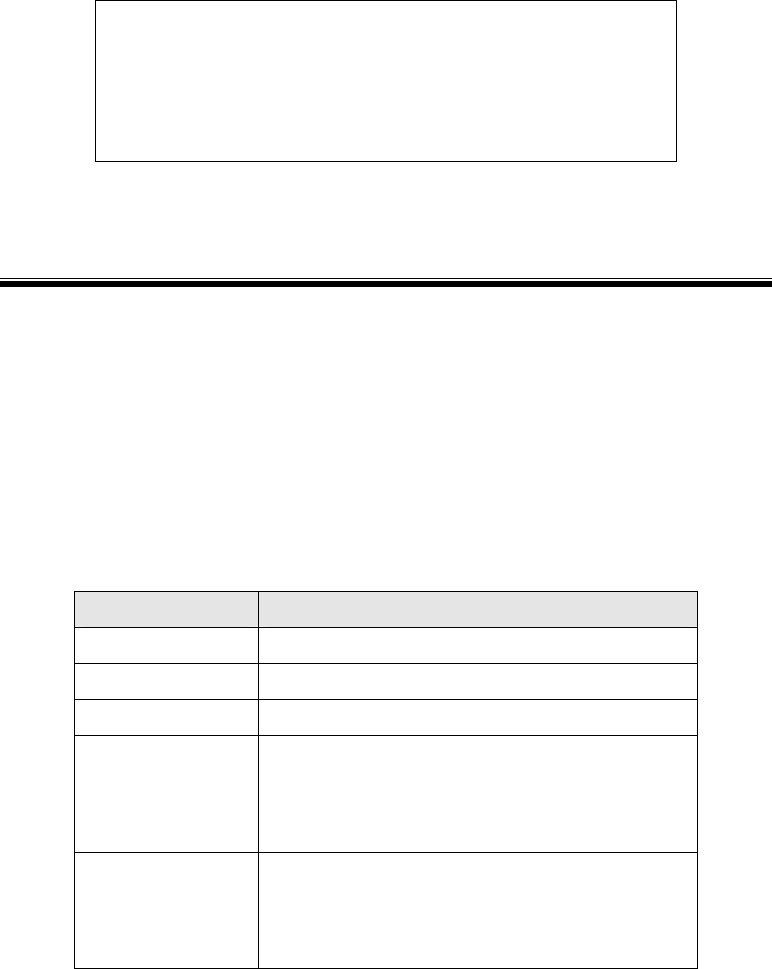
4. Use the following data to complete the resulting dialog.
Field Data
Name Enter a name for this printer
Spool Directory /var/spool/lpd/name_of_printer
File Limit 0 (no limit)
Remote Host Name or IP Address of Wireless Print Server
e.g. SC3000014
Note: host file entry is required to use the name
instead of IP Address
Remote Queue Ln
Where n is the Logical Printer number
By default, L1 is port 1, and L2 is port 2 if the Print
Server has 2 ports.
5. Save this data, and exit the Printer Configuration. Configuration is now completed, and the
printer is now available for use.
Page 71