ES-2024 Series User’s Guide
263 Appendix B IP Addresses and Subnetting
The following table shows the network number and host ID arrangement for classes A, B and
C.
An IP address with host IDs of all zeros is the IP address of the network (192.168.1.0 for
example). An IP address with host IDs of all ones is the broadcast address for that network
(192.168.1.255 for example). Therefore, to determine the total number of hosts allowed in a
network, deduct two as shown next:
• A class C address (1 host octet: 8 host bits) can have 2
8
– 2, or 254 hosts.
• A class B address (2 host octets: 16 host bits) can have 2
16
– 2, or 65534 hosts.
A class A address (3 host octets: 24 host bits) can have 2
24
– 2 hosts, or approximately 16
million hosts.
IP Address Classes and Network ID
The value of the first octet of an IP address determines the class of an address.
• Class A addresses have a 0 in the leftmost bit.
• Class B addresses have a 1 in the leftmost bit and a 0 in the next leftmost bit.
• Class C addresses start with 1 1 0 in the first three leftmost bits.
• Class D addresses begin with 1 1 1 0. Class D addresses are used for multicasting, which
is used to send information to groups of computers.
• There is also a class E. It is reserved for future use.
The following table shows the allowed ranges for the first octet of each class. This range
determines the number of subnets you can have in a network.
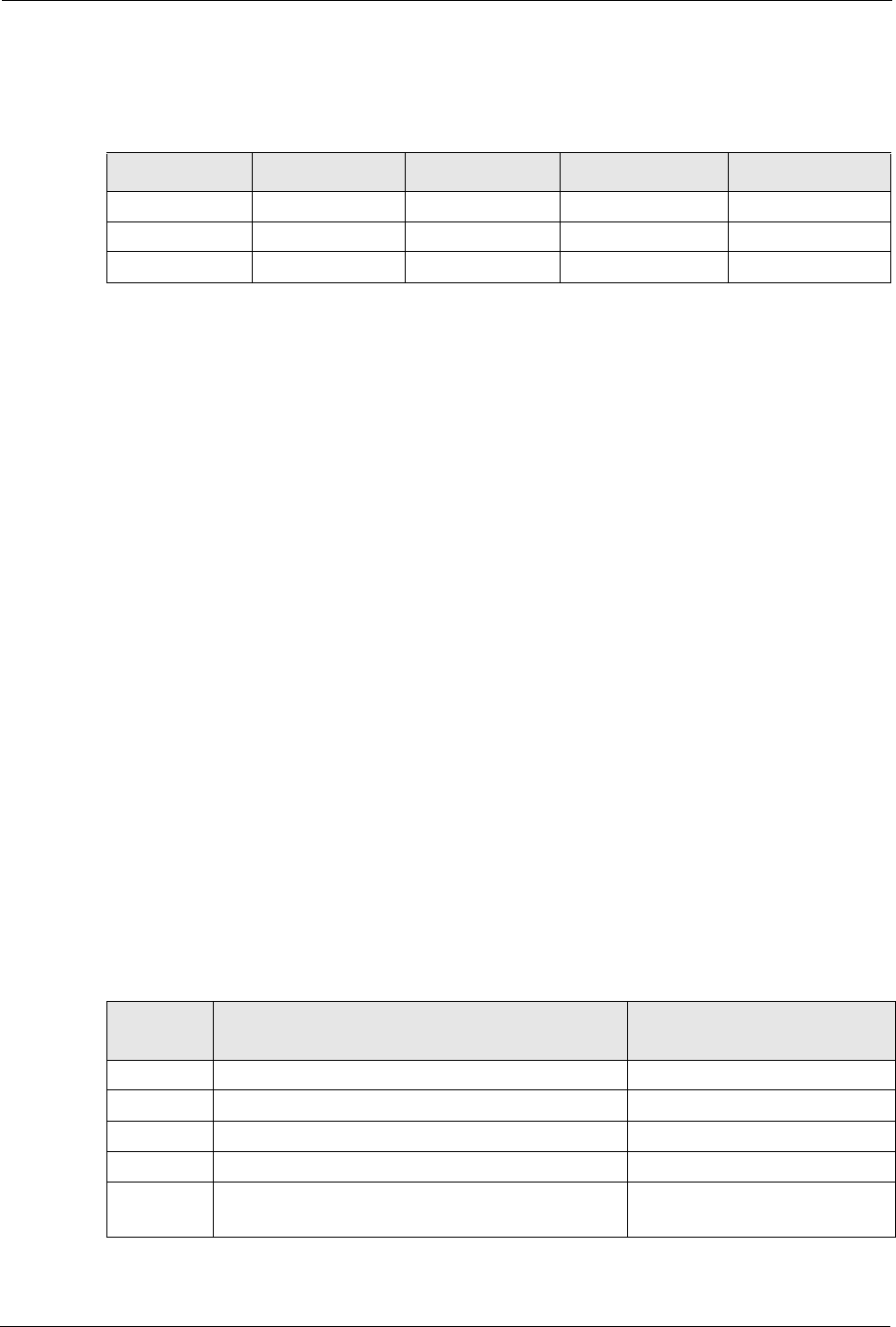
Table 82 Classes of IP Addresses
IP ADDRESS OCTET 1 OCTET 2 OCTET 3 OCTET 4
Class A Network number Host ID Host ID Host ID
Class B Network number Network number Host ID Host ID
Class C Network number Network number Network number Host ID
Table 83 Allowed IP Address Range By Class
CLASS ALLOWED RANGE OF FIRST OCTET (BINARY)
ALLOWED RANGE OF FIRST
OCTET (DECIMAL)
Class A 00000000 to 01111111 0 to 127
Class B 10000000 to 10111111 128 to 191
Class C 11000000 to 11011111 192 to 223
Class D 11100000 to 11101111 224 to 239
Class E
(reserved)
11110000 to 11111111 240 to 255


















